France Web Accessibility
In today's globalized world, the concept of accessibility is essential to ensure equal rights for all individuals. In France, the commitment to accessibility is reflected in the laws and initiatives designed to facilitate the inclusion of people with disabilities in various aspects of life. This article outlines the accessibility laws in France, the impact of digital accessibility on disabled individuals, the importance of accessibility in public transport, the requirements for website accessibility, and the protection of disabled people's rights in the country.
What are the accessibility laws in France?
France has made significant strides in formulating laws to ensure accessibility for people with disabilities. The 2005-102 law, also known as the "Loi Handicap," was a pivotal legislation that aimed to improve the living conditions and inclusion of people with disabilities. This law mandated various actions to be taken by public and private establishments to make them fully accessible to all individuals. Additionally, the law emphasized the importance of RGAA compliance, which refers to the General Accessibility Requirements for Administrations, ensuring that digital services and platforms are accessible to everyone. Non-compliance with accessibility laws can have legal implications, leading to penalties for establishments that fail to adhere to the regulations.
How does digital accessibility impact disabled people in France?
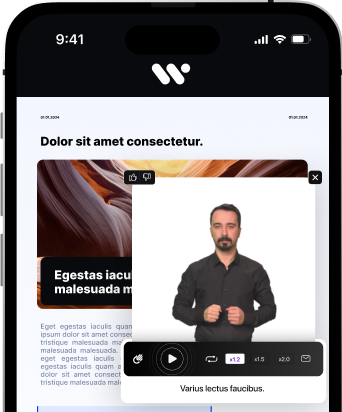
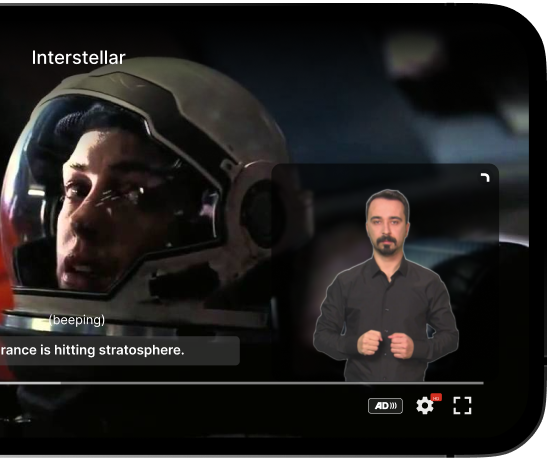
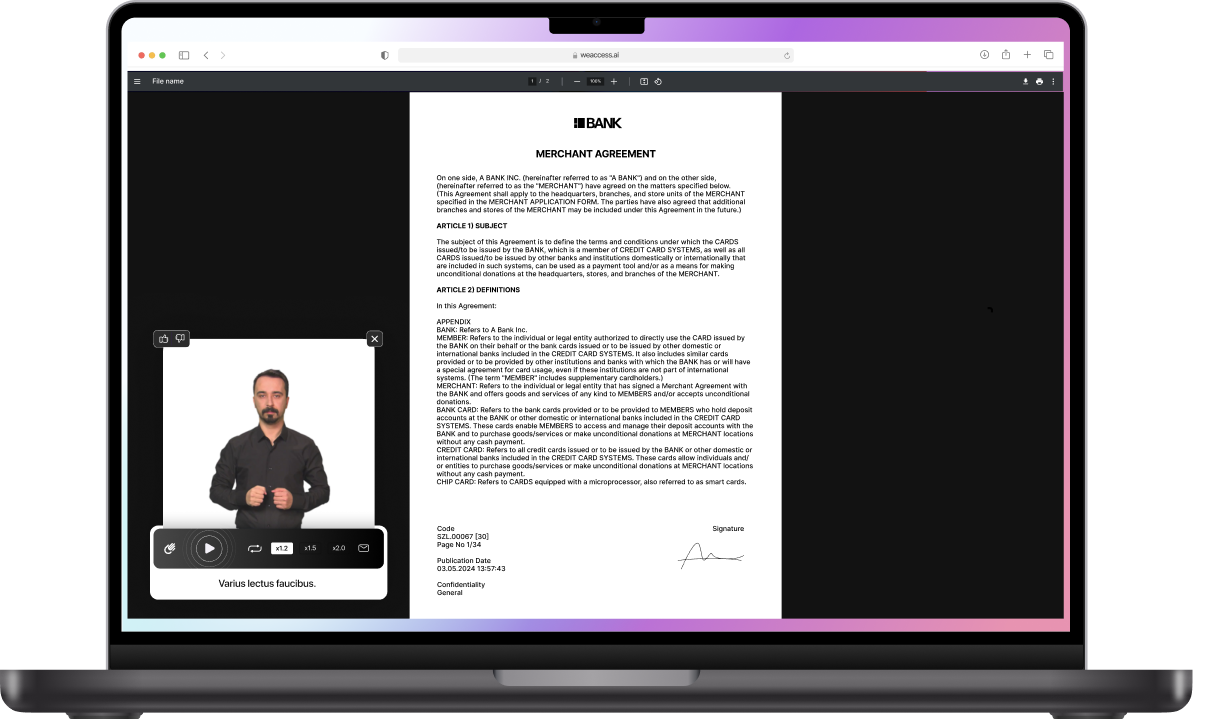
and services. The visual impairment, hearing disabilities, motor impairments, and cognitive limitations faced by these individuals can create barriers to accessing information and participating in digital activities. Therefore, adherence to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) is crucial for websites and online services to ensure they are accessible to people with disabilities. Assistive technology, such as screen readers and speech recognition software, plays a vital role in enabling digital accessibility for individuals with disabilities, bridging the gap and providing them with equal access to digital content.
Why is accessibility important for public transport in France?
Improving the accessibility of public transport is essential for promoting inclusivity and ensuring that individuals with disabilities can travel independently. Wheelchair users face challenges in accessing transportation services, and it is crucial to enhance provisions for them. Similarly, visually impaired individuals require specialized accommodations to navigate public transport safely. Initiatives aimed at making public transport more inclusive involve implementing tactile markings, audible announcements, and priority seating for people with disabilities. These efforts are part of a broader commitment to create an inclusive transportation system that caters to the diverse needs of all individuals, including those with disabilities.
What are the accessibility requirements for websites in France?
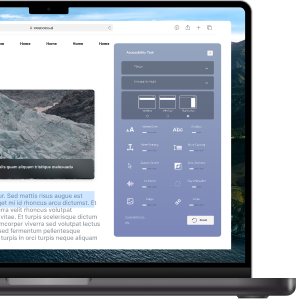
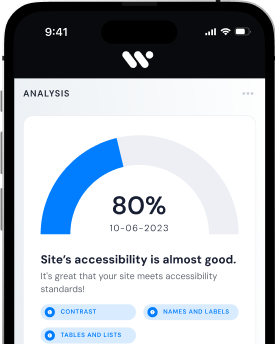
Websites in France are required to adhere to specific guidelines to ensure accessibility for all users. Making a website accessible involves considering various factors, such as providing alternative text for images, ensuring keyboard navigation, and designing content that is perceivable and operable by individuals with disabilities. Several tools are available to scan websites for accessibility compliance and identify areas that need improvement. The upcoming 2024 requirements for digital accessibility further emphasize the commitment to creating inclusive online experiences for all users, regardless of their abilities.
How are the rights of disabled people protected in France?
The rights of disabled people are safeguarded in France through the n° 2005-102 legislation, which sets the framework for promoting equality and establishing mechanisms to address accessibility issues. Various initiatives and organizations, such as APF France Handicap and the National Conference on Disabilities, work towards improving accessibility and advocating for the rights of people with disabilities. Despite these efforts, challenges related to inaccessible environments persist, highlighting the need for continuous work to ensure that all individuals have equal opportunities and access to services, employment, and public spaces.
you may be interested in EU Accessibility!