Accessibility Examples: Inspiring Accessible Websites
Accessible website examples can inspire others to incorporate accessibility features into their own web design. By considering navigation, color contrast ratio, and keyboard navigation, designers can create accessible web pages that are accessible to people with disabilities. Screen readers and assistive technologies can also help improve the user experience for those with visual impairments or low vision.
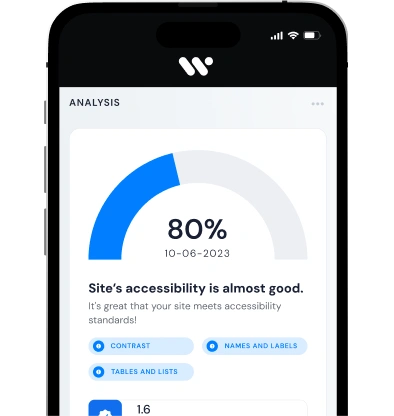
Some of the most accessible websites like the BBC website meet accessibility standardstext for images and ensuring that the site is accessible through keyboard navigation for those who do not use a mouse. Accessibility testing is crucial in designing a website that is accessible to everyone.
Understanding Accessibility
Accessibility refers to providing equal access to all individuals, regardless of any physical accessibility barriers. This is achieved through accessible design and adherence to accessibility standards such as wcag compliance. Website accessibility means making your website accessible to everyone, including those with fine motor control issues. By incorporating accessibility features like text for images, you can make your content accessible to a larger audience.
Creating an accessible website involves providing accessible navigation, free website accessibility tools, and accessibility help for users to navigate easily. Some examples of accessible websites to inspire your organization’s website include those that prioritize website accessibility and follow the standards for web accessibility set by the web accessibility initiative. Conducting an accessibility scan on your website for accessibility can reveal any accessibility issues that need to be addressed.
Alt Text and Its Importance
Accessibility is essential for creating an accessible website examples to inspire and great web accessibility examples. One important aspect of accessibility is the use of alt text for images, which ensures that visually impaired individuals can still understand the content of a website. Additionally, incorporating accessible web design examples like proper heading structures, color contrast for those with color blindness, and wheelchair accessible features can greatly enhance the user experience for all visitors.
Another key component of accessibility best practices is regularly using an accessibility scanner to check for any common accessibility issues. Accessibility solutions such as providing accessibility training for content creators and following a set of web accessibility guidelines can help ensure your website is accessible. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses can create a website that’s accessible to all individuals, leading to a more inclusive online environment.
Disability and Web Accessibility
Web accessibility means ensuring that all users, including those with disabilities, can navigate and interact with a website. Accessibility features such as text alternatives for images, proper heading structure, and color contrast are crucial for creating accessible content. Major accessibility barriers include lack of alt text, poor navigation, and inaccessible forms.
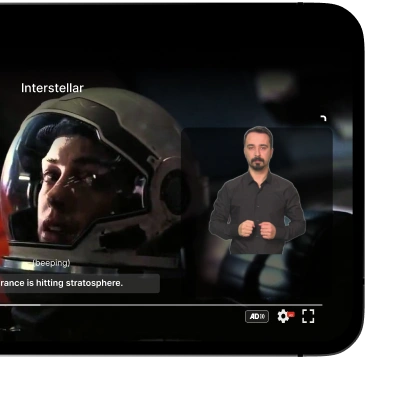
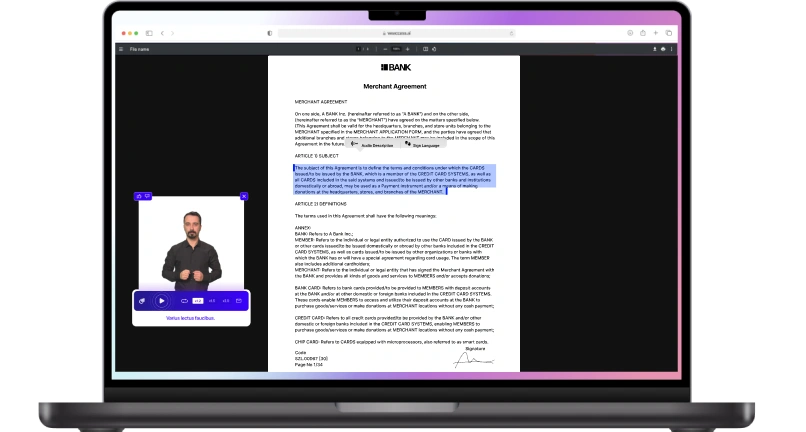
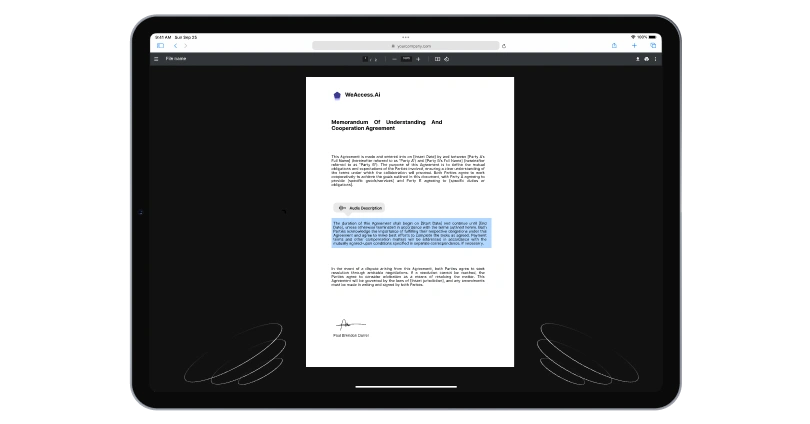
A website also needs to comply with web accessibility standards to provide equal access to all users. Example of accessibility includes providing captions for videos, audio descriptions, and accessible entrance options. Business case for accessibility demonstrates the importance of reaching a wider audience and improving user experience.
Accessibility web design requires web designers to consider the needs of all users. The website features should be designed in a way that the content is accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities. By showing a commitment to accessibility, a website demonstrates a dedication to inclusivity and user satisfaction.
WCAG: Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
Accessibility is the practice of making websites and web applications also accessible to people with disabilities. The accessibility features examples include alternative text for images, proper heading structures, color contrast, and keyboard navigation options.
Keyboard Accessibility
Keyboard accessibility ensures that individuals with physical disabilities can navigate and interact with a website using only a keyboard. This is crucial for making websites inclusive and user-friendly for all. By incorporating keyboard shortcuts and providing keyboard focus indicators, developers can improve the overall accessibility of their websites.
Accessibility Features for Websites
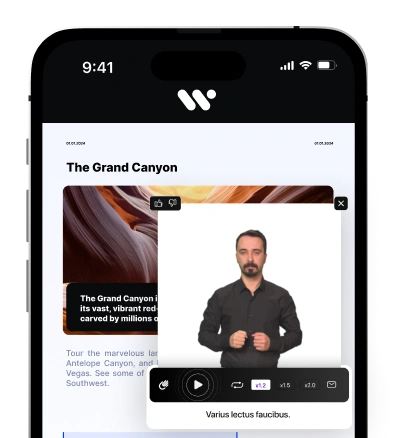
Accessibility features for websites are crucial for ensuring that individuals with disabilities can access and navigate the content effectively. Alt tags provide descriptions for images, keyboard navigation allows users to navigate without a mouse, and captions and transcripts make audio and video content accessible to those with hearing impairments.
Exploring Accessibility Examples
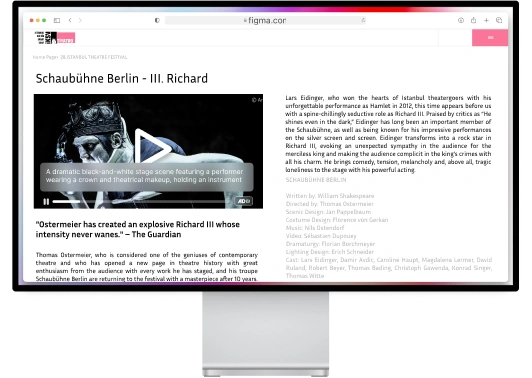
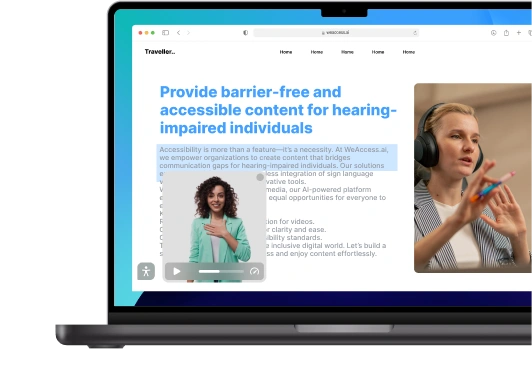
When it comes to exploring accessibility examples, it's important to look at a variety of scenarios. This can include websites with alt text for images, mobile apps with screen reader compatibility, and physical spaces with accessible ramps and doorways. By examining these examples, we can better understand how to create inclusive experiences for all users.
Website Examples for Inspiration
If you're looking for inspiration for your own website, there are countless examples out there to spark your creativity. From e-commerce sites like Amazon to blogging platforms like WordPress, you can find a wide range of styles and designs to draw ideas from.
Study responsive design elements from sites like Apple and Google to see how they adapt to different devices. Pay attention to user experience on sites like Airbnb and Netflix to learn how to create a smooth and intuitive interface for your visitors.
Don't forget to explore innovative design trends on platforms like Behance and Dribbble to stay current with the latest techniques and aesthetics. Take notes on branding strategies from sites like Coca-Cola and Nike to see how they effectively communicate their message through visual elements.
Digital Accessibility: An Overview
Digital Accessibility ensures that websites, software, and documents can be easily accessed and used by individuals with disabilities. It involves making digital content perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users, including those with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments.
Common practices for improving digital accessibility include providing alternative text for images, using clear and simple language, creating navigable structures, and using accessible color contrasts. By following these guidelines, organizations can ensure that their digital products are inclusive and usable for everyone.
Examples Demonstrating Accessibility
1. Screen reader compatibility: Websites and applications that are designed to work with screen readers, allowing users with visual impairments to access content.
2. Keyboard navigation: Providing the ability to navigate through a website or application using only the keyboard, making it accessible for users who cannot use a mouse.
Creating Accessible Websites
Creating accessible websites is essential to ensure that all users, regardless of their abilities, can navigate and interact with your site. This means designing with web accessibility standards in mind, such as using alt text for images and providing keyboard navigation options.
Access for All: Equal Accessibility
Access for All: In order to promote equal accessibility, it is crucial to ensure that individuals of all abilities have the same opportunities to access services, facilities, and information. This includes providing accommodations for those with disabilities, such as ramps, elevators, and braille signage.
Furthermore, implementing technology solutions, like screen readers and captioning services, can help make digital content more accessible to individuals with visual or auditory impairments. By prioritizing equal accessibility, we can create a more inclusive and equitable society for all.
Writing an Accessibility Statement
Writing an Accessibility Statement is crucial for ensuring that your website is inclusive and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. It demonstrates your commitment to providing equal access to information and services, and helps users understand how to navigate your site effectively.
When creating an Accessibility Statement, be sure to include information about the accessibility features of your website, such as alt text for images, keyboard navigation options, and text resizing capabilities. You should also provide contact information for users to report any accessibility issues and outline your plans for ongoing accessibility improvements.
Consider consulting with individuals with disabilities or accessibility experts when drafting your Accessibility Statement to ensure that it effectively addresses the needs of all users. Regularly review and update your statement as needed to reflect changes in your website and advancements in accessibility technology.
By taking the time to write a comprehensive Accessibility Statement, you can improve the user experience for all visitors to your website and demonstrate your commitment to creating an inclusive online environment where everyone can access information and services freely.
Websites Designed for Accessibility
Websites designed for accessibility prioritize making their content easily accessible to all users, regardless of any disabilities they may have. This includes incorporating features such as Alt text, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility to ensure that everyone can navigate and interact with the site effectively. By focusing on accessibility, websites can reach a wider audience and provide a better user experience for all visitors.
Web Tools for Accessibility
Web Tools for Accessibility are essential for ensuring that websites are usable for all individuals, regardless of any disabilities they may have. These tools help developers test for accessibility compliance, make necessary adjustments to improve user experience, and adhere to web accessibility standards.
Resources and Organizations
Resources such as tools, information, and materials are essential for organizations to operate efficiently and effectively. They help enhance productivity and achieve goals. Organizations rely on resources like funding, technology, and human capital to carry out their missions and deliver services. Collaboration with other organizations and leveraging shared resources can also be beneficial.
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is an international community that develops standards to ensure the long-term growth of the web. It is responsible for creating guidelines and protocols that promote compatibility and interoperability of web technologies. The organization works to make the web accessible and inclusive for all users.
Great Examples of Web Accessibility
Great examples of web accessibility include websites that provide alt text for images, keyboard navigation for those who cannot use a mouse, color contrast for users with visual impairments, and captions for videos to assist those who are deaf or hard of hearing.
You may be interested: Discover key elements to make , Embracing inclusive design to improve , ADA Accessibility Widget for Websites