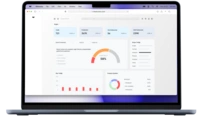
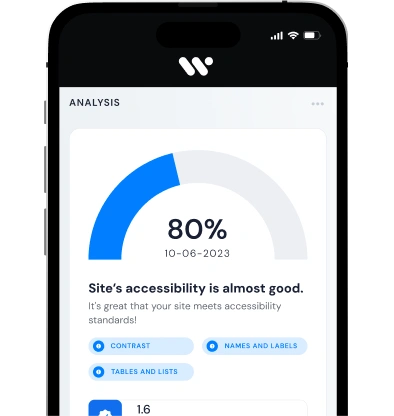
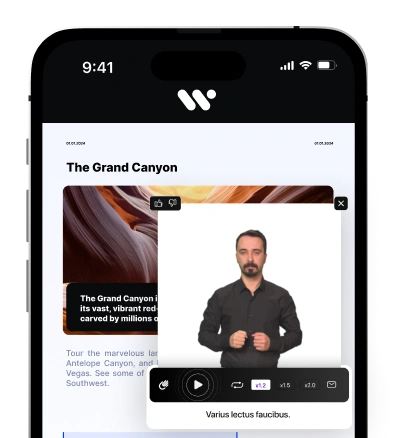
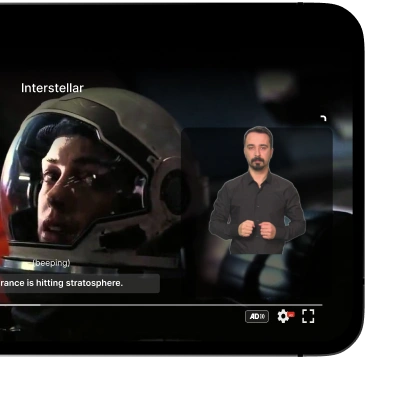
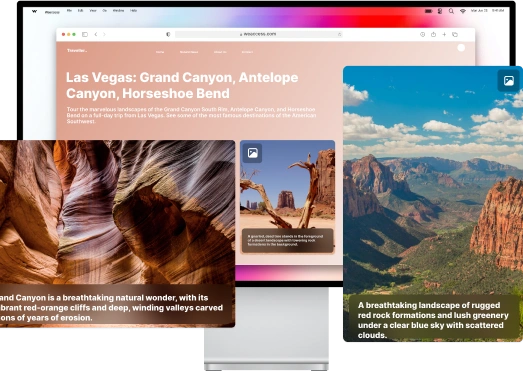
Accessible e-commerce means designing every element—from alt text, keyboard navigation, and high-contrast visuals to WCAG-compliant forms—so that all users, including those with disabilities, enjoy seamless shopping. This inclusive approach not only fulfills legal obligations like the ADA and the European Accessibility Act, but also boosts SEO, reduces bounce rates, increases conversions, and cultivates brand trust and loyalty.
What is Ecommerce Accessibility?
Ecommerce accessibility means designing online stores to be usable and navigable by all customers, including those relying on assistive technologies like screen readers or keyboard navigation.Digital accessibility in this context ensures visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive limitations don’t hinder shopping experiences—helping to avoid legal risks and expand market reach.
Focusing on accessibility in e commerce builds trust, boosts conversions, and strengthens brand reputation while supporting compliance with regulations like the ADA and EU mandates .
Who Wins with Ecommerce Accessibility? Customers, Businesses, and Beyond
- People with disabilities gain access to inclusive online shopping experiences without barriers.
- Shoppers benefit from an equal online shopping experience, improving satisfaction and trust.
- B2C ecommerce stores reach wider audiences, increasing sales and loyalty.
- B2B ecommerce platforms enhance usability, building stronger professional relationships.
Accessibility Features that Define an Inclusive Store
- Accessible design ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can navigate and interact with the website effectively.
- Text size adjustments allow users to modify font sizes for better readability, accommodating those with visual impairments.
- Descriptions provide detailed information about products, aiding users who rely on screen readers or have cognitive disabilities.
From Abandoned Carts to Higher Conversions: The Business Case for Accessibility
- Accessibility and conversions: Accessible websites reduce friction, leading to higher conversion rates by accommodating users with disabilities.
- Conversion rates: Companies that prioritize accessibility can experience significant improvements in conversion rates, as accessible design enhances user experience and satisfaction.
- Market reach: Over 1.3 billion people worldwide have some form of disability; making your website accessible opens doors to this significant market segment.
- Accessibility as competitive advantage: Investing in accessibility not only ensures compliance but also positions businesses as leaders in inclusivity, enhancing brand reputation and customer loyalty.
The Role of Accessible Checkout in Reducing Cart Abandonment
Accessible checkout processes help minimize cart abandonment mid-navigation by ensuring all users, including those with disabilities, can easily progress through each step .
Optimizing forms, buttons, and navigation for cart abandonment at checkout improves completion rates, increases conversion rates, and creates a more inclusive shopping experience
Why Accessible Design Builds Lasting Trust with Shoppers
- Prioritizing inclusive design ensures that all users, including people with disabilities, can interact seamlessly with your site, fostering loyalty
- Enhancing user experience UX through accessibility reduces frustration and improves satisfaction, encouraging repeat visits
- Protecting and promoting brand reputation by demonstrating commitment to accessibility builds consumer trust and differentiates businesses from competitors
Boosting Search Rankings with Accessibility: The Hidden SEO Advantage
- Integrating SEO and accessibility ensures that search engines can effectively index content, improving visibility and driving organic traffic .
- Enhancing ecommerce UX accessibility creates a seamless, user-friendly experience, reducing bounce rates and signaling quality to search engines.
- Accessible websites naturally improve content discoverability and user engagement, boosting overall SEO performance.
Accessibility Standards & Guidelines for Ecommerce
WCAG Demystified: The Core Accessibility Standards for Online Stores
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) define how to make web content more accessible for all users, including those with disabilities. Online stores following these guidelines improve inclusive online shopping experiences and user satisfaction, while reducing legal risk.
|
Standard / Principle |
Key Features |
Ecommerce Application |
Purpose / Benefit |
|
WCAG 2.0 |
Text alternatives, keyboard navigation, color contrast, readable content |
Ensure product images have alt text, forms are navigable via keyboard |
Provide foundational accessibility and legal compliance |
|
WCAG 2.1 |
Mobile accessibility, low vision support, cognitive accessibility |
Optimizes checkout pages and mobile product catalogs for all users |
Enhance inclusive online shopping experiences across devices |
|
WCAG 2.2 |
Improved focus indicators, accessible forms, authentication guidance |
Streamlines login, registration, and checkout flows |
Reduce cart abandonment mid-navigation and improve usability |
WCAG Conformance Levels
|
Level |
Description |
Example Implementation |
|
A (Minimum) |
Meets the basic accessibility requirements. |
Simple text alternatives, basic navigation, basic color contrast. |
|
AA (Recommended) |
Recommended standard for most websites. |
Product pages, forms, and checkout optimized to meet the needs of most users. |
|
AAA (Maximum) |
Highest level of accessibility. |
Advanced content descriptions, high-contrast options, fully inclusive interactive elements. |
POUR Principles (Accessibility Principles)
|
Principle |
Description |
Example Implementation |
|
Perceivable |
Ensures content can be seen and heard by all users. |
Adjustable text sizes, use of alt text for images, sufficient color contrast. |
|
Operable |
Ensures the interface can be used through multiple input methods. |
Navigation via keyboard, touchscreen, or voice commands. |
|
Understandable |
Ensures content and navigation are easy to comprehend. |
Clear and simple language, logical menu structure, consistent page layout. |
|
Robust |
Ensures content works across different technologies and devices. |
Compatibility with modern browsers, screen readers, and other assistive technologies. |
ADA Compliance for Ecommerce: What Every U.S. Business Must Know
- ADA compliance ecommerce ensures that online stores meet the requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act Title III, making digital platforms accessible to all users, including people with disabilities.
- Ecommerce ADA compliance helps businesses avoid ADA legal consequences, including lawsuits and penalties, while improving customer trust and satisfaction.
- Implementing accessible navigation, forms, images, and checkout flows not only reduces legal risk but also enhances inclusive online shopping experiences and broadens market reach.
European Accessibility Act 2025 & Global Laws
- The European Accessibility Act 2025 ecommerce requires online stores in EU member states to meet defined accessibility standards, ensuring that digital products and services are usable by all .
- Compliance with legal requirements under this act includes accessible navigation, forms, media, and checkout processes, similar to WCAG standards.
- Understanding and adhering to accessibility laws globally helps businesses reduce legal risk, improve inclusive online shopping experiences, and expand international market reach.
Section 508 and Ecommerce: Meeting Government-Level Standards
Section 508 compliance mandates that federal agencies’ digital platforms—including ecommerce websites serving government contracts or public users—are fully accessible to people with disabilities. This covers all aspects of the site: content, navigation, forms, multimedia, and interactive elements.
Emphasis for Public/US E-Commerce Sites:
Ecommerce platforms that sell to government employees or handle public contracts must meet Section 508 standards to remain eligible for federal business opportunities. Compliance ensures that all users, including those with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments, can access product information, complete purchases, and interact with the site without barriers. Prioritizing Section 508 not only avoids legal and contractual risks but also demonstrates social responsibility, increases usability, and broadens the potential customer base in the public sector.
Benefits of 508 accessbility
- Section 508 compliance requires that federal agencies’ digital platforms, including ecommerce websites, be fully accessible to people with disabilities, covering content, navigation, and interactive elements.
- Achieving accessibility compliance for online businesses ensures that ecommerce stores meet government-level standards, reduces legal risk, and provides inclusive online shopping experiences for all customers.
- Implementing accessible forms, navigation, multimedia, and checkout processes supports compliance and enhances user satisfaction and market reach.
Accessibility as a Competitive Advantage in Global Markets
Prioritizing accessibility in global markets allows businesses to create inclusive online shopping worldwide, reaching users of all abilities across different regions and cultures. Companies that integrate accessibility into their ecommerce strategy gain a competitive edge through accessibility, enhancing customer loyalty, expanding market share, and building a reputation as socially responsible and forward-thinking.
How Small Accessibility Fixes Can Boost Conversions Overnight
Implementing simple accessibility fixes can lead to a significant ecommerce conversion boost by removing barriers for users with disabilities. Focusing on accessibility and conversions, even minor adjustments like improving navigation, adding descriptive alt text, or enhancing form usability can create smoother shopping experiences. Quick accessibility improvements often result in immediate gains in engagement and sales, demonstrating that conversion optimization accessibility is both a practical and profitable strategy
Statistics That Prove Accessibility Drives E-Commerce Success
Investing in ecommerce accessibility yields substantial returns. A 2022 Forrester Research report found that every $1 spent on accessibility and user improvements brings back up to $100, highlighting the significant ROI of web accessibility .(https://www.boia.org/blog/roi-of-web-accessibility) Moreover, companies with robust accessibility programs experience 28% higher revenue growth than their competitors .
Real-world examples further underscore these benefits. Tesco's collaboration with the Royal National Institute of Blind People (RNIB) led to a 350% increase in online sales by enhancing their website's accessibility . Similarly, Mayo Clinic's focus on accessible design resulted in increased patient engagement and inclusivity .
Despite these successes, many e-commerce sites still lag in accessibility. A study by Baymard Institute revealed that 94% of the world's largest e-commerce sites are not accessibility compliant, with common issues including inaccessible images, links, and form fields . Addressing these accessibility gaps not only improves user experience but also expands market reach and strengthens brand reputation.
Real-World Accessibility Challenges: Visual, Auditory, Motor & Cognitive Needs
Ecommerce platforms often face barriers that prevent users with disabilities from completing purchases. Visual impairments make it difficult to read small text, poorly contrasted content, or unlabeled images. Auditory impairments create challenges when missing captions or audio cues are relied upon for product descriptions or tutorials. Users with motor impairments may struggle with small buttons, drag-and-drop interfaces, or complex checkout flows. Addressing these issues improves inclusive online shopping experiences, enhances user satisfaction, and ensures compliance with accessibility standards.
Common Web Design Mistakes That Exclude Customers
Retail Website Accessibility Issues
- Poor color contrast – Makes text difficult to read for users with visual impairments.
- Missing alt text – Prevents screen readers from describing images to visually impaired users. Provide descriptive alt text to explain what the image shows. For example: “Red running shoes on a white background.” This allows screen readers to convey the image content to visually impaired users, making the shopping experience fully accessible.
- Non-descriptive links – Links like “click here” confuse users relying on assistive technology.
- Broken Semantic HTML – Misused headings, lists, or landmarks disrupt navigation for screen readers
When semantic HTML elements like headings (H1–H6), lists, or landmarks (header, nav, main, footer) are used incorrectly or skipped, screen readers cannot interpret the structure of a page properly. This disrupts navigation for users relying on assistive technologies, making it difficult to understand content hierarchy or quickly jump to important sections.
- Non-responsive design – Mobile or tablet users with accessibility needs struggle to navigate unoptimized layouts.
Why Shoppers Drop Off: Navigation and Checkout Barriers That Cost Sales
- Keyboard accessibility – Users who rely on keyboards or assistive devices struggle to navigate websites without proper tabbing order or shortcuts.
- Focus indicators – Missing or unclear focus outlines make it hard to see where users are on the page.
- Skip links – Lack of skip navigation links forces repetitive tabbing, frustrating screen reader users.
- Inaccessible checkout forms – Unlabeled form fields or complicated authentication steps (Captcha) prevent successful transactions .
- Accessible checkout process – Streamlined forms, clear labels, and keyboard navigation improve completion rates and reduce cart abandonment.
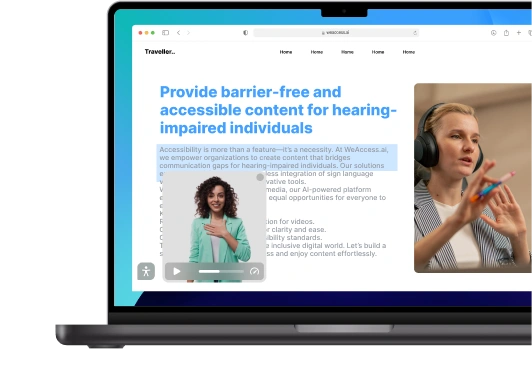
Creating Content Everyone Can Access: Text, Images, Video & Audio
- Alt text for meaningful images – Provide descriptive alternative text so screen readers can convey image content to visually impaired users.
- Screen reader accessibility – Ensure all text, links, and interactive elements are readable by assistive technologies.
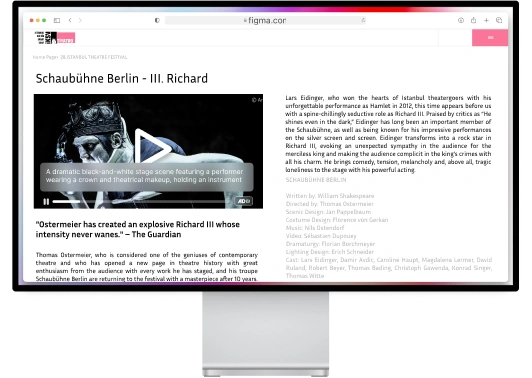
- Accessible images – Use high-contrast visuals, clear labeling, and scalable formats for better visibility. (For example: A “Buy Now” button uses white text on a dark blue background (high contrast) ).
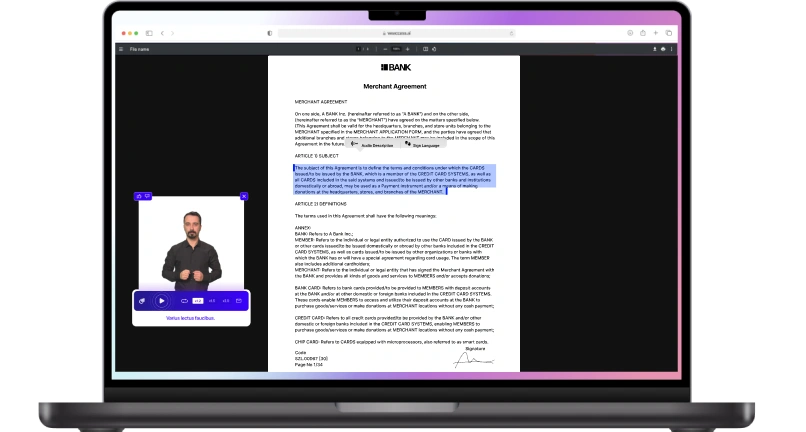
- Accessible videos – Add captions, audio descriptions, and transcript options to support users with auditory or visual impairments .
- Descriptive link text – Avoid generic phrases like “click here”; use meaningful link descriptions for better navigation.
Designing Checkout Flows That Work for All Shoppers
- Accessible forms – Ensure all form fields are labeled correctly and compatible with screen readers.
- Properly structured forms – Use logical field grouping, headings, and clear instructions to guide users through checkout.
- Intuitive navigation – Simplify steps, provide visible progress indicators, and reduce unnecessary clicks to enhance usability.
- Consistent navigation – Maintain uniform menus, buttons, and page layouts across the site to support all users in completing purchases.
Behind the Code: Essential Technical Features for Accessibility
- ARIA landmarks – Implement Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) roles to help screen readers identify page regions and navigation.
- Heading structure – Use a clear, hierarchical heading system (H1-H6) for better navigation and content comprehension.
- Semantic HTML – Properly structure content using semantic elements.
- Responsive accessible design – Ensure layouts adapt to all devices while maintaining readability, navigation, and functionality for all users.
Making Ecommerce Mobile-Friendly and Assistive-Tech Ready
- Mobile accessibility – Ensure that ecommerce websites are fully responsive, with touch-friendly buttons, scalable text, and adaptable layouts for smartphones and tablets.
- Assistive technologies – Optimize websites to work seamlessly with screen readers (e.g., JAWS, NVDA, VoiceOver), voice recognition software accessibility and alternative input devices.
- Screen reader compatibility – Ensure proper ARIA roles, semantic HTML, and descriptive labels so visually impaired users can navigate product pages, forms, and checkout flows effectively.
Accessibility Testing Tools: What Automation Can (and Can’t) Do
- Automated accessibility testing – Use tools to identify common accessibility issues, such as missing alt text, improper headings, or contrast errors, but note that automation cannot catch all user experience problems.
- Accessibility overlays – Software that applies visual or functional fixes can help but may not fully resolve underlying code issues or ensure compliance .
- Accessibility widgets – Widgets can provide features like text resizing or high-contrast modes, improving usability for some users but not replacing proper accessible design.
- Accessibility tool – A comprehensive accessibility tool should combine automated testing, manual review, and user feedback to ensure all barriers are identified and resolved .
Why Real User Testing Matters More Than Automation
While automated accessibility testing can catch common web accessbility issues, manual accessibility audits are essential for identifying nuanced barriers that affect real users. Gathering user feedback from individuals with disabilities provides insights that machines cannot detect, such as confusing navigation, unclear instructions, or cognitive load challenges.
Comprehensive accessibility auditing that combines both manual review and real-world user testing ensures ecommerce sites deliver truly inclusive online shopping experiences and meet legal and usability standards.
The Hybrid Approach: Blending Automated and Human Testing
Hybrid accessibility testing combines the speed of automated tools with the insight of manual audits, ensuring thorough identification of barriers that impact users with disabilities. This approach helps maintain accessibility conformance across all pages while addressing complex usability issues that automation alone cannot detect. Continuous accessibility monitoring through this hybrid method ensures ecommerce websites remain compliant, improve user experience, and support inclusive online shopping experiences over time.
Where to Get Help: Professional Accessibility Services for Ecommerce
For businesses seeking expert guidance, digital accessibility services for ecommerce websites offer tailored solutions to ensure compliance and inclusivity. Accessibility consulting helps identify gaps in design, code, and content, while accessibility training equips teams with the skills to maintain long-term compliance. Publishing an accessibility statement demonstrates commitment to all users and builds customer trust, signaling that your ecommerce platform prioritizes inclusive online shopping experiences
The Legal Risks of Ignoring Accessibility in Ecommerce
Failing to prioritize accessibility exposes ecommerce businesses to accessibility lawsuits ecommerce, which have become increasingly common in the U.S. and other markets. Non-compliance can result in financial penalties, legal fees, and mandated remediation, creating significant business liability and legal risk. By proactively implementing accessible design and functionality, companies reduce their exposure to litigation, enhance customer trust, and demonstrate social responsibility
ADA Demand Letters: What They Mean for Online Retailers
ADA website compliance demand letters are formal notifications sent to businesses highlighting violations of accessibility requirements under the Americans with Disabilities Act. For ecommerce platforms, receiving such a letter signals the need to improve accessibility compliance for e-commerce immediately, as failure to respond can escalate to lawsuits and financial penalties.
Proactively addressing these demands by implementing accessible design and functionality helps protect the brand, reduce legal exposure, and enhance inclusive online shopping experiences.
Staying Compliant: How to Protect Your Business from Accessibility Lawsuits
Regular compliance audits are essential to ensure ecommerce sites meet current accessibility standards compliance, reducing the risk of litigation and fines. Establishing a clear accessibility policy demonstrates commitment to inclusive design and guides ongoing improvements. By continuously monitoring and updating websites to align with legal and technical standards, businesses protect themselves from accessibility lawsuits ecommerce while enhancing user trust and engagement.
The Future of Accessibility: AI, Automation, and Emerging Tools
The future of ecommerce accessibility is increasingly shaped by artificial intelligence and ecommerce automation, enabling faster identification and resolution of accessibility barriers. Emerging technologies provide automated accessibility fixes for images, forms, navigation, and multimedia content, reducing manual workload while improving inclusive online shopping experiences. Integrating AI-driven tools with human oversight ensures that online stores remain compliant, user-friendly, and competitive in global markets.
Raising Awareness: Training and Education for Inclusive Ecommerce
Investing in accessibility training and accessibility education equips ecommerce teams with the knowledge and skills to create fully inclusive digital experiences. Promoting accessibility advocacy within organizations encourages adoption of best practices, while implementing ongoing accessibility initiatives ensures long-term compliance and user satisfaction. Together, these efforts foster a culture that prioritizes inclusive online shopping experiences and strengthens brand reputation.
Accessibility as the Next Growth Engine for Global Ecommerce
Implementing robust accessibility programs and engaging in accessibility collaborations with experts and organizations helps ecommerce businesses expand their reach and improve customer loyalty. Strategic accessibility campaigns raise awareness, attract diverse audiences, and demonstrate social responsibility, positioning accessibility as a key driver of growth. By prioritizing inclusive design, online retailers not only comply with regulations but also unlock new opportunities for inclusive online shopping experiences worldwide
Step-by-Step: Building an Accessible Ecommerce Website
- Assess Current Accessibility – Conduct an audit to identify barriers and areas for website accessibility improvements using both automated tools and manual accessibility audits.
- Plan and Prioritize Improvements – Create a roadmap for implementing changes that address high-impact issues first, aligning with WCAG standards and website legal requirements.
- Optimize Content –Ensure all images have alt text, videos have closed captions/video captions, and links use descriptive text for a fully inclusive experience.
- Enhance Navigation and Forms – Build accessible forms with proper labeling, clear instructions, and intuitive tab order; improve keyboard accessibility and focus indicators for seamless navigation.
- Implement Technical Accessibility Features – Use semantic HTML, ARIA landmarks, and responsive accessible design to ensure assistive technology compatibility.
- Test and Iterate – Combine automated tools with real user testing to validate changes, fix issues, and ensure ongoing ecommerce website accessibility service quality.
- Document and Maintain – Publish an accessibility statement, train staff with accessibility education, and schedule regular audits to maintain compliance and improve inclusive online shopping experiences.
- Reports/statics -In digital accessibility, leveraging reports and statistical insights allows organizations to precisely evaluate website and application inclusivity, uncover usability gaps, and ensure adherence to legal standards. These data-driven assessments not only guide targeted improvements but also quantify the impact of accessibility initiatives on key business outcomes.
- Automation-only solutions / Hybrid approach - Automation-only solutions can quickly identify common web accessibility issues, but they often miss nuanced barriers that affect real users. A hybrid approach, combining tools like Weaccess.ai with manual audits and user testing, ensures comprehensive coverage by detecting both technical errors and experiential challenges. This strategy delivers a robust accessibility solution, optimizing websites for compliance, usability, and inclusive user experiences.
Creating an Accessibility Roadmap for Your Online Business
Developing a structured accessibility plan helps ecommerce businesses systematically meet accessibility requirements and improve user experience. Start by identifying key areas for improvement, then implement targeted accessibility solutions across design, content, and technical components. Organizing initiatives into phased accessibility projects ensures progress is measurable, maintains compliance with legal standards, and fosters inclusive online shopping experiences.
Conclusion
Investing in digital accessibility is no longer optional—it's a critical factor for creating inclusive accessibility that benefits all users and drives business growth. By applying the strategies outlined above, businesses can transform their own ecommerce site into a platform that welcomes everyone, reduces legal risk, and maximizes engagement and conversions. Tools like Weaccess.ai provide automated solutions to streamline accessibility improvements, helping ecommerce sites stay compliant while offering inclusive online shopping experiences.
FAQ
1. Why is accessibility critically alive?
Accessibility is critically alive because it expands market reach, increases conversions, improves user experience, and ensures compliance with laws like the ADA and European Accessibility Act
2. How does web accessibility work?
Web accessibility works by integrating design, content, and technical elements that remove barriers for users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments, ensuring inclusive navigation, readable content, and functional forms.
3. Why Inclusive Online Shopping Builds Brand Loyalty?
Inclusive online shopping fosters trust and loyalty by demonstrating a commitment to all customers, improving usability, reducing abandonment rates, and creating inclusive online shopping experiences that encourage repeat purchases