Inclusive Media for Every Viewer

In today's digital age, web accessibility has become a crucial aspect of designing and developing websites and online content. For the media and entertainment industry, it is essential to ensure that their websites and digital media are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. In this article, we will explore key considerations for web accessibility, inclusive design for media websites, the importance of making entertainment content reach everyone, incorporating assistive technologies effectively, and various legal aspects related to web accessibility in the media and entertainment industry.
Web Accessibility: Key Considerations
Web accessibility refers to the practice of designing websites and online content in a way that enables people with disabilities to perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with the information effectively. It involves creating a digital environment that is inclusive and accommodating to all users, regardless of their abilities.
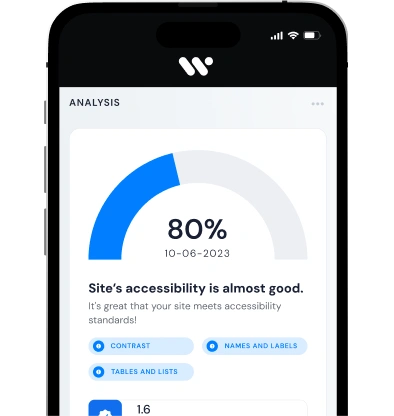
Ensuring web accessibility requires considering various aspects such as providing alternative text for images, using clear and straightforward language, providing captions and transcripts for multimedia content, ensuring keyboard navigation, and implementing logical and consistent website structure. By prioritizing web accessibility, media companies can reach a broader audience and enhance user experience.
Inclusive Design for Media Websites
Media websites play a significant role in delivering news, entertainment, and information to the public. To cater to a diverse audience, media companies should adopt inclusive design principles when developing their websites. This involves creating a user interface that is easy to navigate, readability-friendly, and free from unnecessary distractions.
Inclusive design goes beyond catering to individuals with disabilities; it also considers the needs of users across various devices and internet speeds. By adopting inclusive design practices, media websites can provide a seamless and enjoyable experience for all users, leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
Making Entertainment Content Reach Everyone
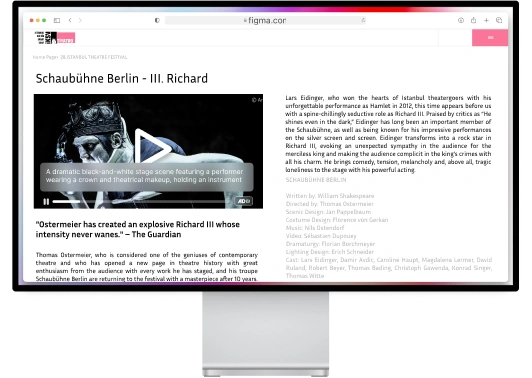
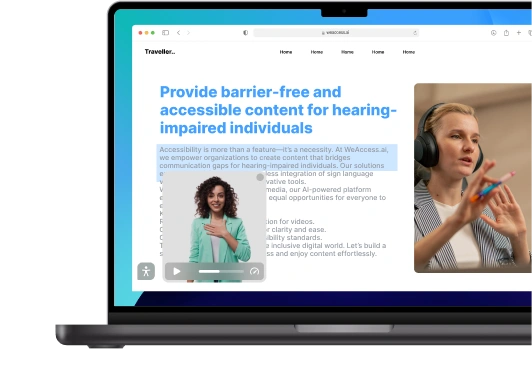
The entertainment industry holds a powerful influence over society and culture. To maximize its impact, it is essential to make entertainment content accessible to everyone. This can be achieved by providing closed captions for videos, offering audio descriptions for visual content, and incorporating sign language integration for video content.
Accessible entertainment content not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enhances the overall viewing experience for all users. It allows media companies to connect with a wider audience and fosters a sense of inclusivity within the entertainment sphere.
Accessibility and Media User Interface
User interface design plays a critical role in ensuring web accessibility. Media companies need to consider the layout, color contrast, and font size to ensure readability for users with visual impairments. Additionally, implementing an intuitive and straightforward navigation system can significantly enhance the user experience.
By prioritizing accessibility in the user interface, media companies can create an inclusive online environment that accommodates users with various needs, resulting in increased engagement and customer satisfaction.
Incorporating Assistive Technologies Effectively
Assistive technologies, such as screen readers, voice recognition software, and alternative input devices, are essential tools for individuals with disabilities to access digital content. Media companies should design their websites and digital media with compatibility for these assistive technologies in mind.
Effective incorporation of assistive technologies ensures that users with disabilities can interact with online content seamlessly. It also demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity and social responsibility, positively impacting the brand image of media companies.
Improving Accessibility of Audio and Video Media
Now that we have explored the key considerations for web accessibility and the significance of inclusive design, let's focus on improving the accessibility of audio and video media.
User-Friendly Video Accessibility
Videos have become a dominant form of content consumption on the internet. To make video content accessible, media companies should provide closed captions and subtitles. This not only benefits individuals with hearing impairments but also allows viewers to follow along in noisy environments or without sound.
Moreover, adding interactive transcripts to videos enables users to search for specific content within the video, enhancing the overall user experience and making information more accessible.
Expanding Audio Media Accessibility
Audio content, such as podcasts and audio articles, is a valuable medium for delivering information and entertainment. To improve the accessibility of audio media, media companies can provide text transcripts for audio content. This allows individuals with hearing impairments to access the information presented in the audio format.
By offering both audio and text versions of content, media companies cater to a broader audience, including those with varying preferences and accessibility needs.
Accessible Video Player Features
Media companies should pay attention to the design and functionality of their video players. Implementing accessible video player features, such as adjustable playback speed, volume controls, and keyboard navigation support, can significantly improve the user experience for all viewers.
Customizable video player settings empower users to personalize their viewing experience based on their preferences and requirements, contributing to an inclusive media environment.
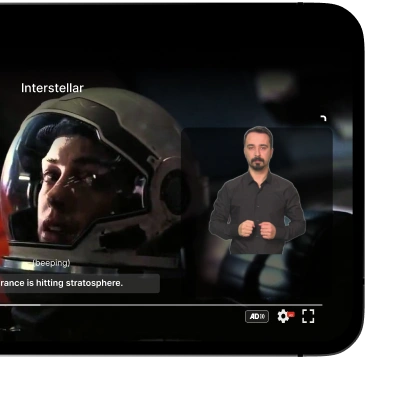
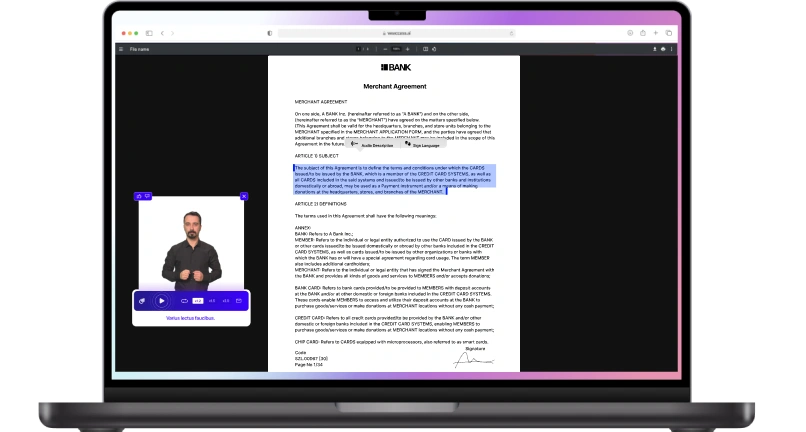
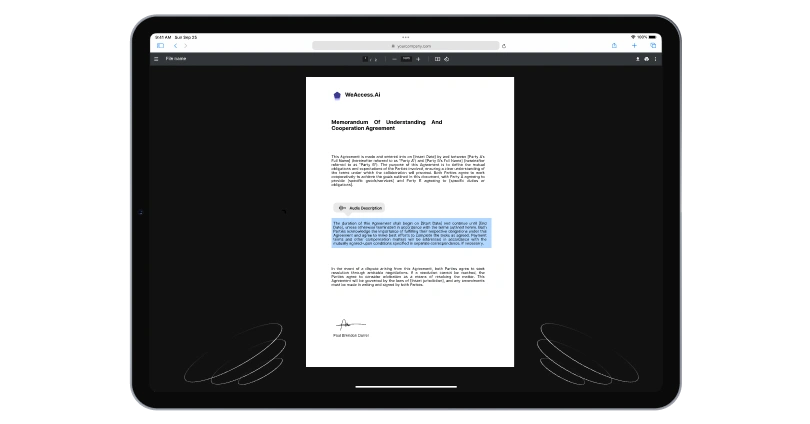
Audio Description for Visual Content
For visually impaired individuals, audio description is a critical accessibility feature. It involves adding narration that describes the visual elements and actions within videos, enabling users to comprehend the content without relying on visuals.
By incorporating audio description, media companies can ensure that visually impaired users can fully engage with their video content, fostering a sense of inclusivity and accessibility.
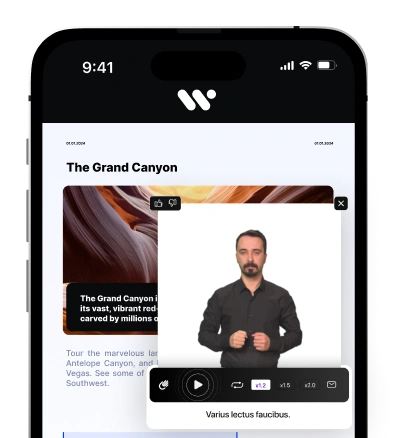
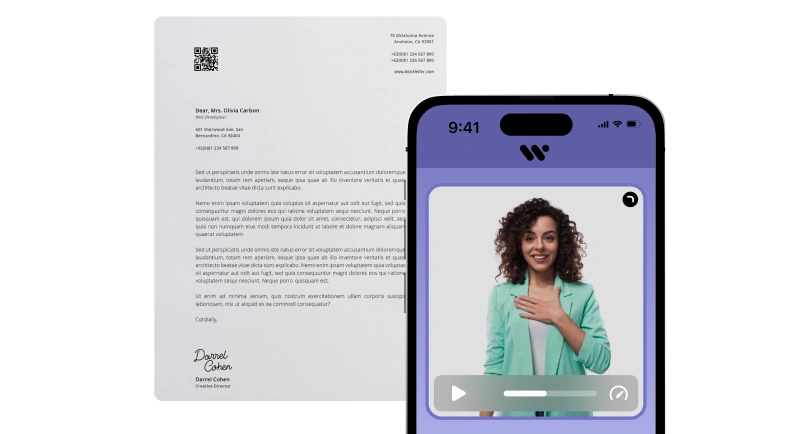
Sign Language Integration in Video
To cater to the deaf and hard-of-hearing community, media companies can integrate sign language interpretation in their video content. This can be achieved by providing videos with sign language overlays or offering separate sign language versions.
By doing so, media companies demonstrate their commitment to inclusivity and create an environment where individuals with hearing disabilities can fully participate in the content.
Web Accessibility Laws for Media and Entertainment
In addition to the ethical and social considerations, there are legal requirements that media companies must adhere to regarding web accessibility. Let's delve into the web accessibility laws and guidelines relevant to the media and entertainment industry.
CVAA and FCC Guidelines Overview
The Twenty-First Century Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) is a significant piece of legislation in the United States aimed at improving the accessibility of communications and video content. The CVAA requires that video programming distributors make their content accessible to individuals with hearing and vision disabilities.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) enforces the CVAA guidelines, ensuring compliance among media companies and video programming distributors.
Complying with Web Accessibility Laws
To ensure compliance with web accessibility laws, media companies must follow the guidelines set forth by their respective countries or regions. The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are widely recognized as the international standard for web accessibility.
By adhering to WCAG guidelines, media companies can meet legal requirements and create an inclusive online environment for all users.
Understanding Digital Accessibility Regulations
Digital accessibility regulations vary from country to country and are continuously evolving. It is essential for media companies to stay informed about the latest regulations and guidelines relevant to their target audience and geographic reach.
By proactively understanding and implementing digital accessibility regulations, media companies can avoid legal challenges and contribute to a more inclusive online ecosystem.
Media Industry ADA Compliance
In the United States, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities. As part of ADA compliance, media companies must ensure that their digital properties, including websites and mobile applications, are accessible to individuals with disabilities.
Ensuring ADA compliance is not only a legal obligation but also an opportunity for media companies to demonstrate their commitment to equal access and social responsibility.
Global Accessibility Standards
As the internet transcends geographical boundaries, media companies must consider global accessibility standards. While specific regulations may vary from country to country, incorporating
universally accepted accessibility practices ensures that content reaches a diverse international audience.
By embracing global accessibility standards, media companies can create a positive and inclusive online experience for users worldwide.
Legal Challenges Faced by Media Companies
Despite efforts to improve web accessibility, media companies may still encounter legal challenges related to accessibility issues. Let's explore some common legal challenges and how media companies can address them effectively.
Media Accessibility Lawsuits Explained
In recent years, there has been a rise in accessibility-related lawsuits targeting media companies with inaccessible digital content. These lawsuits typically allege violations of web accessibility laws and guidelines, such as failure to provide accessible features like closed captions, alt text, or keyboard navigation.
Understanding the basis of such lawsuits can help media companies take proactive measures to prevent legal disputes.
Navigating Web Accessibility Litigations
Legal battles over web accessibility can be complex and resource-intensive for media companies. It is essential for media companies to work with legal experts who specialize in digital accessibility to navigate such litigations effectively.
By proactively addressing accessibility issues and seeking legal counsel, media companies can minimize the risk of costly lawsuits.
Legal Compliance in Media Entertainment
The media and entertainment industry is subject to a wide range of legal regulations, including those related to copyright, licensing, and privacy. In the context of web accessibility, media companies must ensure compliance with both general legal requirements and specific accessibility regulations.
A comprehensive approach to legal compliance, including accessibility, helps media companies mitigate legal risks and maintain a positive reputation.
Addressing ADA Compliance Challenges
ADA compliance can present unique challenges for media companies, particularly when it comes to digital accessibility. Ensuring that all aspects of their digital properties meet ADA standards requires ongoing effort and diligence.
By working with accessibility experts, media companies can identify and address compliance challenges more effectively.
Overcoming Accessibility Lawsuit Risks
To reduce the risk of accessibility-related lawsuits, media companies must prioritize web accessibility from the early stages of website development and content creation. Conducting regular accessibility audits and implementing user testing with individuals with disabilities can help identify and fix potential issues before they escalate into legal disputes.
By being proactive about accessibility, media companies can safeguard their brand reputation and avoid costly legal battles.
Benefits of Making Media and Entertainment Web-Accessible
Making web accessibility a priority offers numerous benefits to media companies beyond legal compliance. Let's explore how a commitment to web accessibility can positively impact media businesses and society as a whole.
Reaching Diverse Audience Segments
Web accessibility enables media companies to connect with a more extensive and diverse audience. By removing barriers to access, content becomes available to individuals with disabilities, different language preferences, and varying internet capabilities.
By catering to a broader audience, media companies can expand their reach and engagement, leading to increased brand visibility and loyalty.
Inclusivity's Impact on Media Consumption
Inclusive web design fosters a sense of belonging and inclusivity among users. When individuals with disabilities can access and engage with digital content seamlessly, it enhances their overall media consumption experience.
Creating an inclusive media environment encourages users to return for more content, share their positive experiences, and recommend the media company to others.
The Business Case for Accessibility
Web accessibility is not just a social responsibility; it also makes good business sense. Media companies that prioritize accessibility experience better brand perception and are more likely to attract socially conscious consumers.
Moreover, accessible websites and content are more likely to rank higher in search engines, leading to increased organic traffic and visibility.
Accessibility and Media Profitability
Investing in web accessibility can yield positive financial returns for media companies. By reaching a broader audience, media companies have the potential to attract more advertisers and generate higher revenues.
Moreover, inclusive design and accessible content can lead to greater user satisfaction, encouraging users to stay longer on the website and engage with more content.
Social Impact of Web Accessibility
Web accessibility plays a significant role in promoting social equality and inclusion. When media companies prioritize accessibility, they send a powerful message about their commitment to equal access and diversity.
By being inclusive, media companies contribute to a more compassionate and empathetic society, making a positive impact on individuals with disabilities and their communities.
Conclusion
Ensuring web accessibility in the media and entertainment industry is not only a legal requirement but also a moral imperative. By adopting inclusive design principles, incorporating assistive technologies, and complying with web accessibility laws, media companies can create a more inclusive online environment that caters to all users, regardless of their abilities.
Prioritizing web accessibility leads to various benefits, including reaching diverse audience segments, fostering inclusivity's positive impact on media consumption, and making a strong business case for accessibility. By considering the social impact of web accessibility, media companies can contribute to a more equitable and inclusive society.
FAQs
1. What is web accessibility?
Web accessibility refers to the practice of designing websites and digital content in a way that allows individuals with disabilities to access and interact with the information effectively.
2. How does web accessibility benefit media companies?
Web accessibility enhances brand perception, expands audience reach, and can lead to increased organic traffic and revenues for media companies.
3. What are the legal challenges faced by media companies in web accessibility?
Media companies may encounter accessibility-related lawsuits and legal disputes if their digital content does not meet web accessibility laws and guidelines.
4. What is the impact of inclusive design on media consumption?
Inclusive design fosters a sense of belonging among users and enhances their overall media consumption experience, leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
5. Why is web accessibility important for society?
Web accessibility promotes social equality and inclusion, making it easier for individuals with disabilities to access information and participate fully in digital spaces.
6-What is media accessibility?
Media accessibility refers to the practice of making various forms of media, such as audio, video, and text content, accessible to individuals with disabilities. It involves providing features like closed captions, audio descriptions, and transcripts to ensure equal access to media for all users.
7-What makes media accessible?
Media accessibility is achieved by incorporating features that cater to the needs of individuals with disabilities. This includes adding closed captions and subtitles for videos, providing audio descriptions for visual content, and offering transcripts for audio content.
8-What is the accessibility of digital media?
The accessibility of digital media refers to how well online content, such as websites, videos, and audio files, can be accessed and used by individuals with disabilities. It involves implementing design elements and features that accommodate various disabilities, ensuring equal access and usability for all users.


 Web Accessibility Suite
Inclusive, accessible web for all.
Web Accessibility Suite
Inclusive, accessible web for all.


 Mobile Accessibility Suite
Smooth access on mobile devices.
Mobile Accessibility Suite
Smooth access on mobile devices.


 Media Accessibility Suite
Accessible videos and images for all.
Media Accessibility Suite
Accessible videos and images for all.


 Document Accessibility Suite
Accessible PDFs for all.
Document Accessibility Suite
Accessible PDFs for all.


 Printed Content Accessibility Suite
Accessible print, audio description, voiceover, & sign language support.
Printed Content Accessibility Suite
Accessible print, audio description, voiceover, & sign language support.