European Accessibility Act (EAA) — What You Need to Know Before 2025
The European Accessibility Act (EAA), taking effect on 28 June 2025, introduces EU-wide accessibility standards for key products and services, from e-commerce and banking to transport and ICT. Its goal is to create a unified market, improve inclusion for people with disabilities, and reduce compliance costs across member states.
Understanding the European Accessibility Act and Its Legal Power
The European Accessibility Act (EAA), officially known as Directive (EU) 2019/882, was adopted by the European Parliament on 17 April 2019 and took effect on 28 June 2025. This directive aims to improve the functioning of the internal market for accessible products and services by removing barriers created by divergent rules in different member states. It also seeks to enhance access for persons with disabilities and the elderly, aligning with the EU's commitment to the UN's Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
Applicability and Scope
The EAA applies to a wide range of products and services, including personal devices such as computers, smartphones, e-books, and TVs, as well as public services like television broadcasts, automated teller machines (ATMs), ticketing machines, public transport services, banking services, and e-commerce sites.
Global Applicability
Organizations based outside the EU that offer products or services within the EU market must also comply with the directive's accessibility requirements
Implementation and Enforcement
Member states were required to transpose the EAA into national law by 28 June 2022. Enforcement is carried out through market surveillance by individual EU nations, with penalties for non-compliance varying by country
Impact Assessment and Updates
The European Commission conducted an impact assessment prior to the adoption of the EAA to evaluate its potential effects. Ongoing updates and guidelines are provided to assist organizations in achieving compliance
Critical Deadlines and Compliance Dates You Can’t Miss
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) enforces strict compliance timelines for businesses operating in the EU.
📅 Key Deadlines
- June 28, 2025: The primary compliance date. All new products and services placed on the EU market after this date must meet the EAA's accessibility requirements
- June 28, 2027: Emergency services must meet accessibility requirements
- June 28, 2030: Existing products and services already on the market before June 28, 2025, must comply by this date or their next update, whichever comes first.
- June 28, 2045: Long-life self-service terminals (e.g., ATMs, ticketing machines) installed before June 28, 2025, must comply within 20 years of installation or by this date, whichever comes first.
It's crucial for businesses to audit their products and services, adopt the necessary accessibility standards, and establish ongoing processes to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal and financial repercussions.
Compliance, Enforcement, and How to Avoid Costly Penalties
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) mandates that businesses offering digital products or services in the EU must comply with accessibility standards, regardless of their location
Compliance Steps
To ensure compliance and avoid penalties:
- Conduct Accessibility Audits: Perform comprehensive audits using both automated tools and manual testing to identify and address accessibility issues
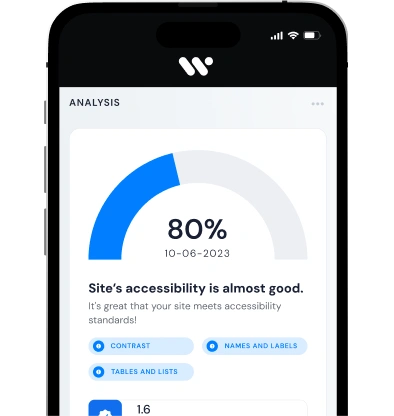
- Implement Necessary Changes: Based on audit findings, make required adjustments to digital content, ensuring adherence to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 Level AA.
- Publish an Accessibility Statement: Provide a clear and concise statement outlining the accessibility features and compliance status of your digital products or services.
- Engage in User Testing: Involve individuals with disabilities in testing to gain valuable insights into real-world accessibility challenges.
- Regular Monitoring and Updates: Continuously monitor accessibility and update digital content to maintain compliance as standards evolve.
Enforcement and Penalties
Non-compliance with the EAA can result in significant penalties, including fines ranging from €5,000 to €20,000 per violation. Additionally, businesses may face reputational damage and restricted market access within the EU.
To mitigate risks, businesses should proactively integrate accessibility into their digital strategies, ensuring compliance and fostering an inclusive user experience.
Accessibility Standards and Guidelines You Must Follow
To comply with the European Accessibility Act (EAA), businesses must adhere to specific accessibility standards:
- EN 301 549: This European standard outlines technical accessibility criteria for Information and Communication Technology (ICT) products and services, including websites, mobile apps, and hardware. It incorporates the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 Level AA and is being updated to align with WCAG 2.2.
- WCAG 2.2: The latest version of the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), introduces additional success criteria to enhance digital accessibility. While WCAG 2.2 is not yet harmonized in EN 301 549, aligning with its guidelines is considered a best practice for future compliance.
For comprehensive compliance, consider conducting accessibility audits, obtaining certification, and providing a clear accessibility statement. Utilizing tools like VPAT (Voluntary Product Accessibility Template) and incorporating alt text for images can further support your efforts. Regular user testing ensures that your digital products are usable by individuals with disabilities, aligning with the EAA's objectives.
Products and Services Covered Under the EAA
Digital Products and Technologies Covered by the European Accessibility Act
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) mandates that various digital products and technologies be accessible to individuals with disabilities across the EU. This includes:
- Operating Systems: Software platforms that manage hardware and software resources on devices.
- Smartphones and Mobile Phones: Devices enabling voice calls, text messaging, and access to communication apps.
- Computers: Desktops and laptops used for various digital tasks.
- TV Equipment: Television sets and related broadcasting services
- E-books: Digital versions of books accessible on various devices
- E-commerce Platforms: Online retail services and websites.
- Websites and Mobile Apps: Digital interfaces for various services and information.
- Telephony Services: Communication services, including VoIP and traditional telephony.
- Software: Applications and programs used across devices.
These requirements apply to both public and private sector entities operating within the EU, as well as those outside the EU offering services or products to EU consumers .
Physical Goods and Packaging Rules Under the European Accessibility Act
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) mandates that manufacturers ensure their physical products and packaging are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes:
- Product Identification: Each product must bear a type, batch, or serial number, or another identifier. If this is not possible due to the product's size or nature, the information must appear on the packaging or in accompanying documentation.
- Manufacturer Information: The manufacturer's name, registered trade name or trademark, and contact address must be clearly visible on the product, or if impractical, on its packaging or in a document accompanying the product.
- Instructions and Safety Information: Clear and understandable instructions and safety information must be provided in a language easily understood by consumers in each Member State where the product is made available.
These requirements aim to ensure that products and their packaging are accessible and usable by all consumers, including those with disabilities, thereby promoting inclusivity and compliance within the EU market.
Industries and Sectors Most Impacted by the European Accessibility Act
The European Accessibility Act (EAA), effective from June 28, 2025, mandates that various sectors ensure their products and services are accessible to individuals with disabilities. Key industries affected include:
- Banking and Financial Services: Institutions must make their websites, mobile applications, ATMs, payment terminals, and customer support services accessible, adhering to the EAA's standards.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers are required to ensure that their digital platforms, including appointment booking systems and patient portals, are accessible to all users.
- Transport Services: Airlines, railways, and public transportation services must provide accessible booking systems, real-time information, and physical infrastructure to accommodate passengers with disabilities.
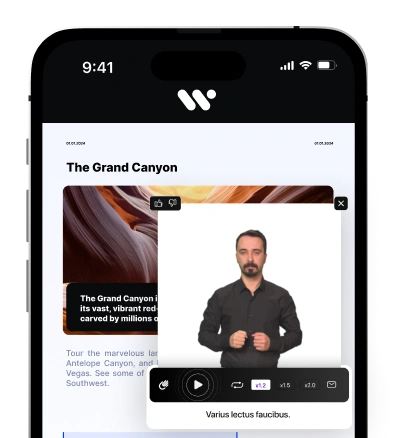
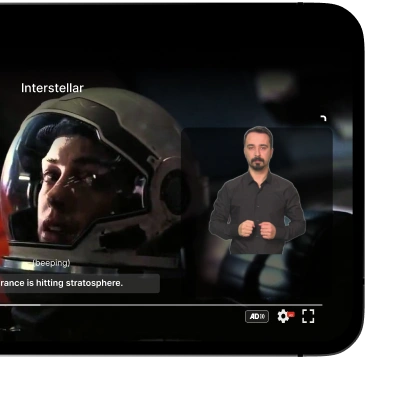
- Media and Broadcasting: Television broadcasters and streaming services are obligated to offer accessible content, including subtitles, audio descriptions, and sign language interpretation.
These sectors must comply with the EAA's accessibility requirements to ensure equal access and participation for individuals with disabilities across the European Union.
Physical and Digital Access Points That Must Be Accessible
Under the European Accessibility Act (EAA), effective June 28, 2025, all new self-service terminals in the EU must meet strict accessibility standards. This includes
- Automated Teller Machines (ATMs): Must feature audio-assisted transactions, such as headphone jacks and voice-guided menus, to assist visually impaired users.
- Ticketing Machines: Should provide tactile interfaces, clear audio instructions, and visual adjustments to accommodate users with various disabilities.
- Check-in Machines: Must be designed with accessibility in mind, offering features like adjustable screen heights and alternative input methods.
- Self-Service Kiosks: Require multi-sensory alerts, text-to-speech capabilities, and tactilely discernible keys to ensure usability for all customers.
These measures aim to create an inclusive environment, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can independently access and use these services.
Countries and Regions Within the EAA Scope
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) applies to all 27 EU member states, including:
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Portugal
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- Finland
- Hungary
- Malta
- Romania
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Sweden
- Poland
- Czech Republic
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Estonia
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Croatia
- Ireland
- Greece
- Luxembourg
- Sweden
Additionally, the EAA applies to non-EU entities that provide goods or services to EU consumers, including businesses in the UK, Switzerland, and Norway. This means that companies based in these countries must comply with the EAA if they sell or distribute products or services within the EU market
Accessibility by Design — Tools and Strategies for Success
Implementing accessibility by design ensures that digital products are usable by individuals of all abilities, aligning with both ethical standards and legal mandates like the European Accessibility Act (EAA). This approach integrates accessibility into the design process, rather than treating it as an afterthought.
Key Strategies and Tools
- Inclusive UX Design: Adopt an inclusive design strategy that considers the diverse needs of all users, including those with disabilities. This involves creating digital experiences that cater to a wide range of abilities from the outset, ensuring accessibility is embedded throughout the design process.
- User-Centered Research: Conduct inclusive user research by engaging with individuals representing a broad spectrum of disabilities. Develop user personas and scenarios to understand how users with various disabilities will interact with the product, guiding design decisions.
- Accessibility Guidelines: Follow established accessibility standards such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and EN 301 549, which provide comprehensive criteria for making digital content accessible
- Assistive Technologies: Utilize tools like WAI-ARIA to enhance the accessibility of web applications, ensuring that dynamic content and user interface components are accessible to users with disabilities.
- Continuous Testing and Feedback: Regularly test designs with real users, including those with disabilities, to identify and address accessibility issues early in the design process. Incorporate feedback to refine and improve the user experience.
By integrating these strategies and tools, organizations can create digital products that are not only compliant with accessibility mandates but also provide an inclusive and equitable user experience for all
European Accessibility Act FAQ
1. What is the European Accessibility Act (EAA)?
The European Accessibility Act is an EU directive that sets accessibility requirements for a wide range of products and services — from smartphones and ATMs to e-commerce websites and transport apps — to ensure they are usable by people with disabilities across member states.
2. Does the European Accessibility Act apply to the UK?
No — since Brexit, the UK is not required to follow the EAA. However, UK sellers to the EU and non-EU organizations serving EU customers must comply if they want market access within the EU.
3. Who does the European Accessibility Act apply to?
The EAA applies to businesses with 10 or more employees, B2B and B2G suppliers, and organizations providing accessible products and services in the EU market. Micro-enterprises have certain exemptions under national law.
4. When does the European Accessibility Act apply?
The compliance deadline is June 28, 2025. EU countries had until June 28, 2022 to transpose the directive into national law, and there is a transition period before enforcement.
5. Is the European Accessibility Act mandatory?
Yes — for covered products and services within the EU market. Businesses must ensure compliance or face fines, penalties, and possible restrictions on selling in the EU.
6. How to comply with the European Accessibility Act?
Compliance involves meeting WCAG 2.2 and EN 301 549 standards, providing accessibility statements, accessible packaging and labeling, and conducting accessibility audits and user testing.
7. How will the European Accessibility Act be enforced?
Enforcement is carried out by national authorities through compliance monitoring, audits, and penalties for non-compliance. The European Commission oversees harmonized EU standards.
8. How will the European Accessibility Act impact small businesses?
Small businesses may face challenges in training, implementing accessibility measures, and updating digital accessibility for websites and mobile apps. Micro-enterprises may have reduced requirements.
9. Does the European Accessibility Act require both subtitles and captions?
Yes — media streaming, telephony services, and electronic tickets must meet accessibility requirements, including subtitles, captions, and real-time information where applicable.
10. Which European languages are mandatory under the Accessibility Act?
Language requirements depend on national law and the member state where the product or service is offered, but instructions and accessibility statements must be understandable within the EU.
11. What are the main goals of the European Accessibility Act?
The EAA aims to ensure accessible products and services for people with disabilities, harmonize standards across the EU, and improve market access for businesses through digital inclusion.
12. How to prepare for the European Accessibility Act?
Start by conducting an accessibility audit, reviewing WCAG and EN 301 549 requirements, updating websites, mobile apps, and packaging, training teams, and ensuring all services are accessible before June 2025.