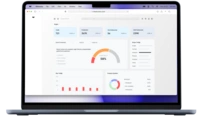
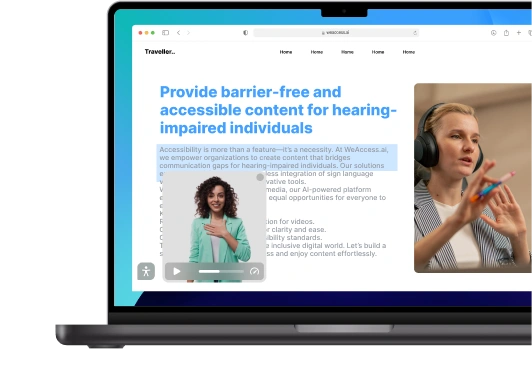
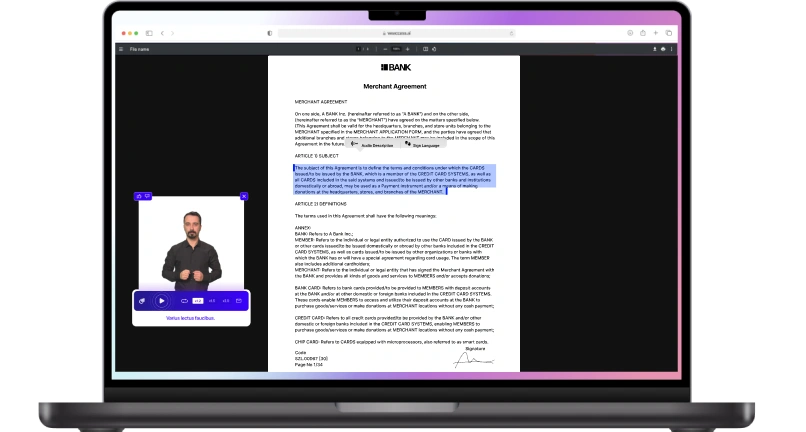
Web accessibility is a crucial aspect of digital inclusion in the UK. As the internet plays an increasingly vital role in everyday life, it is essential to ensure that websites and mobile applications are accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities. In this article, we will explore the key accessibility laws in the UK, how accessibility requirements apply to public sector bodies, the main principles of web accessibility, conducting an accessibility audit for websites, and the importance of prioritizing web accessibility for public sector websites.
What are the key accessibility laws in the UK?
Overview of accessibility regulations
Accessibility regulations in the UK are primarily aimed at ensuring that digital content is accessible to all individuals, irrespective of their disabilities. These regulations encompass various aspects of web accessibility, including the design, content, and functionality of websites and mobile applications.
Understanding the Equality Act 2010
The Equality Act 2010 is a pivotal legislation that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities. It requires public sector organizations and service providers to make reasonable adjustments to accommodate people with disabilities, including ensuring the accessibility of their digital content.
Public sector website accessibility laws
Specific accessibility regulations for public sector websites have been established to ensure that government websites are accessible to all users. These regulations are in line with the government's commitment to digital inclusion and accessibility for all.
How do accessibility requirements apply to public sector bodies?
Accessibility standards for public sector bodies
Public sector bodies are obligated to adhere to specific accessibility standards to ensure that their digital content is accessible. This involves implementing the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to guarantee that their websites and mobile applications are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for users with disabilities.
Complying with accessibility laws in the UK
Public sector bodies must comply with the accessibility laws in the UK, including the Equality Act 2010 and the accessibility regulations 2018. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure that digital content is accessible to all individuals, regardless of their abilities.
Publishing an accessibility statement for public sector websites
It is a requirement for public sector organizations to publish an accessibility statement for their websites, detailing the level of compliance with accessibility standards and outlining any areas that do not meet the required accessibility criteria. This transparency is essential for demonstrating the organization's commitment to accessibility and outlining plans for addressing any accessibility issues.
Creating a Monitoring System
Establishing a robust monitoring system involves determining the frequency and scope of accessibility scans, devising processes for remediation of identified issues, and integrating accessibility monitoring as a routine part of the development and maintenance lifecycle.
Manual Accessibility Testing
In addition to automated scanning tools, manual accessibility testing by experts remains indispensable in identifying nuanced accessibility barriers that may not be adequately detected by automated evaluation tools, ensuring a higher level of overall accessibility.
What are the main principles of web accessibility?
Key WCAG 2.1 guidelines for website accessibility
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 provide comprehensive guidance for ensuring web accessibility. These guidelines include criteria for making content perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust, thereby ensuring that websites and mobile applications are accessible to individuals with disabilities.
What must be considered for websites and mobile applications?
When addressing web accessibility, it is vital to consider the specific requirements for both websites and mobile applications. This involves ensuring that the design, functionality, and user interface of both platforms are optimized to meet the accessibility needs of all users, including those with disabilities.
Meeting the accessibility standards for service accessibility
Service accessibility is a key component of web accessibility, particularly for public sector bodies. It involves ensuring that online services provided by government organizations are accessible to all individuals, thereby promoting inclusivity and equal access to essential services.
How to conduct an accessibility audit for websites?
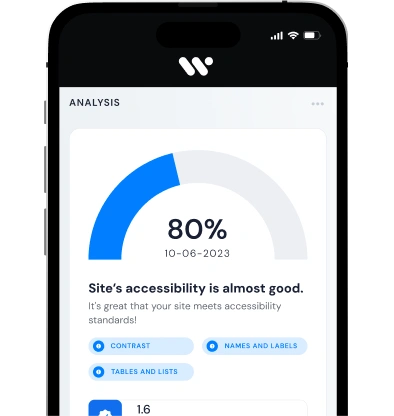
Importance of accessibility audits for digital accessibility
Accessibility audits play a crucial role in evaluating the accessibility of websites and identifying areas that may not meet the required standards. These audits involve comprehensive assessments of the website's design, content, and functionality to ensure compliance with accessibility regulations.
Creating reasonable adjustments for people with disabilities
As part of the accessibility audit process, it is important to identify and implement reasonable adjustments to make websites and mobile applications accessible to people with disabilities. This may involve modifying the design, improving navigation, and providing alternative formats for content.
Meeting level AA of the WCAG guidelines
Conducting an accessibility audit involves striving to meet level AA of the WCAG guidelines, which sets specific criteria for accessibility across various aspects of web content. This level of compliance is crucial for ensuring that digital content is accessible to a wide range of users, including those with disabilities.
Why is it essential for public sector websites to prioritize web accessibility?
Impact of disability discrimination act on digital accessibility
The Disability Discrimination Act 1995 has brought about significant changes in the approach to digital accessibility, emphasizing the importance of making digital content accessible to individuals with disabilities. This has prompted public sector organizations to prioritize web accessibility to comply with the legal requirements and promote inclusivity.
Accessibility requirements and the public sector's responsibility
The public sector holds a significant responsibility in ensuring that its digital content is accessible to all individuals. By prioritizing web accessibility, public sector websites demonstrate their commitment to equal access and inclusivity, aligning with the legal and ethical requirements for accessibility.
Benefits of making websites and mobile applications accessible
Prioritizing web accessibility for public sector websites and mobile applications yields numerous benefits, including broader reach and engagement with diverse user groups, improved user experience, and compliance with accessibility laws and regulations. Additionally, accessible digital content reflects positively on the organization's commitment to equality and diversity.
How the UK accessibility legislation and WCAG 2.2 fit together
The UK accessibility legislation and WCAG 2.2 fit together in the sense that the legislation references the WCAG guidelines as a benchmark for digital accessibility standards. WCAG 2.2 provides specific technical requirements and best practices for making web content more accessible to people with disabilities, aligning with the UK's commitment to ensuring equal access to digital services for all individuals. The legislation reinforces the importance of following WCAG guidelines to achieve accessibility compliance.
Think about accessibility from the start
In the UK, legislation requires that companies make their websites accessible to everyone. It's important for businesses to think about accessibility from the start, rather than as an afterthought. By including a clear accessibility statement on their website and following common web accessibility guidelines, companies can ensure that their online presence is accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities.
You may be interested website accessibility standards