Prepare for the European Accessibility Act

European Accessibility Act (EAA) – Complete Guide & Compliance
What is the European Accessibility Act (EAA)?
The EU Accessibility Act, also known as the European Accessibility Act 2025, is a crucial European Union Directive aimed at standardizing accessibility requirements across the EU. Adopted by the European Commission and approved by the European Parliament, this legislation ensures that essential services like web accessibility, e-commerce, and banking comply with universal design principles.
Advocated by organizations such as the European Disability Forum, it aligns with the Web Accessibility Directive to create an inclusive digital and physical environment under the broader Accessibility Legislation framework.
Why is the European Accessibility Act Important?
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) is pivotal in ensuring accessibility by harmonizing accessibility requirements across the EU. It addresses accessibility barriers by setting unified standards, thereby improving accessibility standards and promoting functional accessibility. This legislation mandates full accessibility for various products and services, leading to increased accessibility for individuals with disabilities
Scope of the European Accessibility Act
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) mandates that various products and services be accessible to individuals with disabilities. Products and services covered include banking services, e-commerce platforms, self-service technologies & kiosks, software & digital products, and websites & mobile applications. The EAA applies to both B2B & B2C services, ensuring comprehensive accessibility across sectors.
Compliance & Requirements for EAA
To achieve EAA compliance, organizations must adhere to harmonized accessibility standards across the EU. This involves aligning with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1, as outlined in the EN 301 549 standard, which serves as the technical blueprint for accessible ICT. Meeting these specific accessibility requirements ensures that digital content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users
How to Comply with the European Accessibility Act
To ensure compliance with the European Accessibility Act (EAA), organizations should:
- Conduct Accessibility Audits: Assess your digital assets to identify and address accessibility issues.
- Implement AI-Powered Accessibility Tools: Utilize AI-driven solutions to automate compliance checks and enhance digital content accessibility
- Prioritize Accessibility: Integrate accessibility considerations into your development processes to ensure all digital content is accessible
- Provide Alt Text for Images: Ensure all images have descriptive alt text to support users relying on screen readers.
European Accessibility Act (EAA) Deadlines & Implementation
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) introduces new standards to ensure accessibility across the EU. It mandates that a range of products and services, including consumer electronics, ticketing and vending machines, websites, and mobile applications, comply with accessibility requirements for persons with disabilities
The implementation of the EAA is scheduled for June 28, 2025. By this date, all relevant products and services placed on the EU market must meet the accessibility requirements outlined in the Act. Organizations are encouraged to begin preparations promptly to ensure compliance by the deadline.
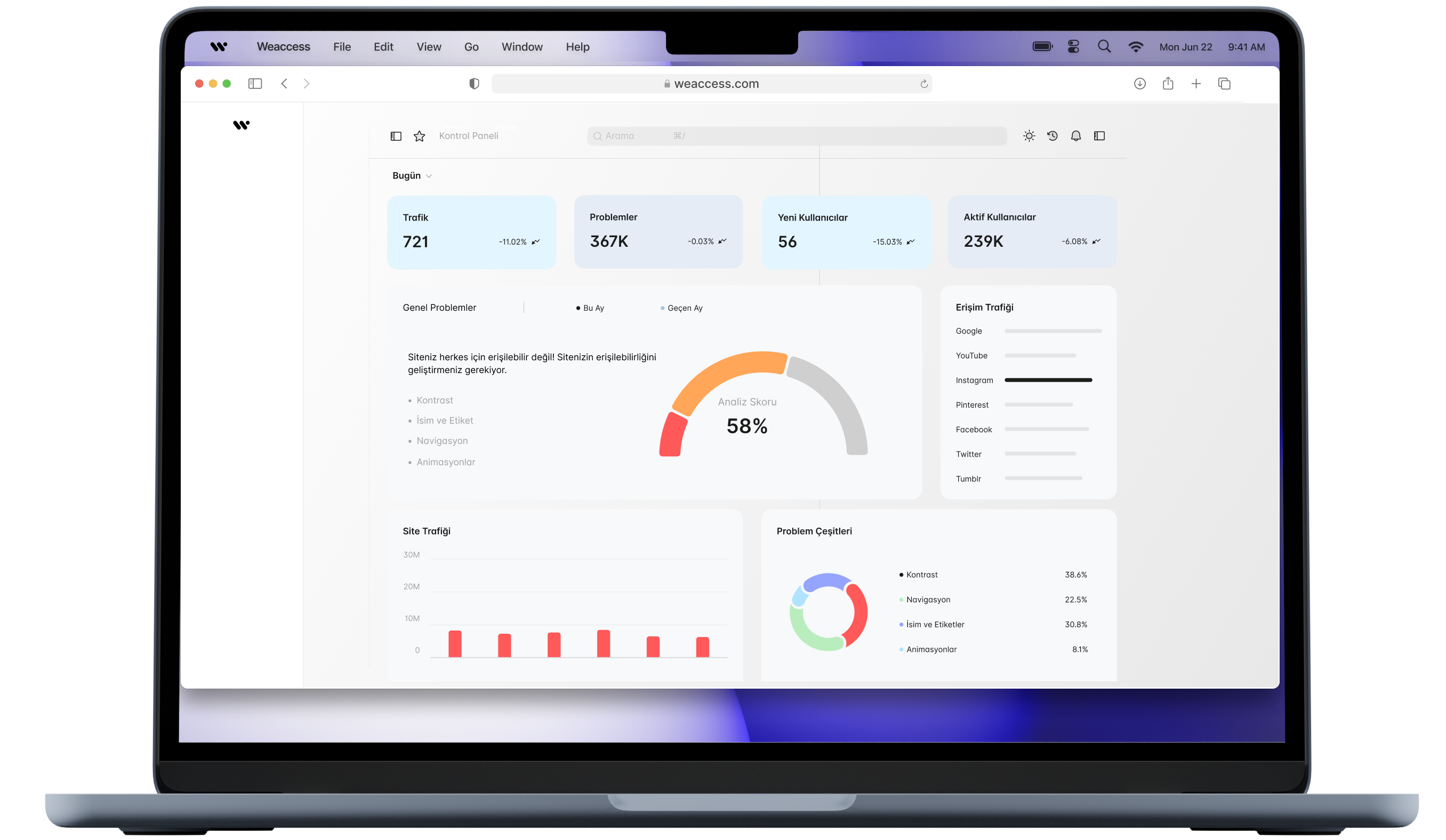
Accessibility Testing & Certification
Ensuring compliance with the European Accessibility Act (EAA) involves rigorous accessibility testing and obtaining appropriate certification. A key standard in this process is EN 301 549, which outlines the accessibility requirements for Information and Communication Technology (ICT) products and services
EN 301 549: Accessibility Requirements
EN 301 549 specifies the technical criteria that ICT products and services must meet to be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This standard supports the European Directive 2016/2102 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies, commonly known as the Web Accessibility Directive
Testing Methods
To comply with EN 301 549, organizations should conduct comprehensive accessibility testing, which includes:
- Automated Testing: Utilizing specialized tools to identify common accessibility issues.
- Manual Testing: Engaging accessibility experts to evaluate the user experience and identify issues that automated tools may miss.
- User Testing: Involving individuals with disabilities to provide feedback on the accessibility of products and services.
These methods collectively ensure that ICT products and services are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users.
Certification
Achieving certification demonstrates an organization's commitment to accessibility. For instance, TÜV SÜD offers a certification mark for digital accessibility of software, indicating that the product has been tested independently and meets the applicable accessibility requirements based on EN 301 549 and the corresponding W3C Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
Accessibility Statements
Organizations are also required to publish an accessibility statement detailing the level of compliance with accessibility standards, indicating any inaccessible content, and providing accessible alternatives
Penalties & Legal Consequences for Non-Compliance
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) mandates that businesses ensure their products and services meet accessibility standards to accommodate individuals with disabilities. Non-compliance with these standards can result in significant penalties, which vary across EU member states.
Complaint Process & Monitoring
The EAA requires member states to establish mechanisms for monitoring compliance and handling complaints. Individuals can file complaints with national authorities if they encounter inaccessible products or services. These authorities are responsible for investigating complaints and ensuring that businesses take corrective actions
European Accessibility Act in Different EU Member States
EAA in Major EU Countries
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) aims to harmonize accessibility standards across the EU, ensuring equal access to products and services for individuals with disabilities. While the EAA sets overarching requirements, its implementation and enforcement are managed at the national level, leading to variations across member states.
France
In France, the EAA is integrated into the existing framework of accessibility laws. The French government has established guidelines to align national regulations with the EAA's provisions, focusing on enhancing accessibility in public spaces and digital platforms. Businesses are encouraged to consult the French Ministry of Solidarity and Health for detailed compliance information.
Germany
Germany has incorporated the EAA into its national legislation, emphasizing the removal of barriers in both physical and digital environments. The Federal Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs oversees the implementation, providing resources and support to businesses for compliance. Detailed information is available on the ministry's official website.
Ireland
Ireland has adopted the EAA, focusing on improving accessibility in public services and digital content. The Department of Children, Equality, Disability, Integration, and Youth is responsible for overseeing the implementation, offering guidance to organizations on meeting accessibility standards.
Italy
Italy has aligned its national laws with the EAA, aiming to enhance accessibility across various sectors. The Ministry of Labour and Social Policies provides resources and support to assist businesses in understanding and complying with the new requirements.
The Netherlands
The Netherlands has integrated the EAA into its accessibility framework, focusing on both physical infrastructure and digital services. The Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Sport oversees the implementation, offering guidance to ensure compliance with accessibility standards.
Belgium
Belgium has adopted the EAA, emphasizing the removal of barriers in public spaces and digital platforms. The Federal Public Service Social Security is responsible for overseeing the implementation, providing resources to assist businesses in meeting accessibility requirements.
Denmark
Denmark has incorporated the EAA into its national legislation, focusing on enhancing accessibility in public services and digital content. The Ministry of Employment oversees the implementation, offering guidance to organizations on complying with accessibility standards.
For comprehensive and up-to-date information, businesses should consult the official websites of the relevant national authorities in each country. These resources provide detailed guidance on compliance requirements, deadlines, and support available to assist in meeting the EAA's standards.
EAA & EU Member States
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) is a directive adopted by the European Union (EU) to harmonize accessibility standards across its member states, ensuring equal access to products and services for individuals with disabilities. By establishing common rules, the EAA aims to eliminate barriers created by divergent national regulations, thereby enhancing the functioning of the internal market for accessible products and services
EU Accessibility
The EAA addresses accessibility requirements for a broad range of products and services, including:
- Computers and Operating Systems
- Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), Ticketing, and Check-In Machines
- Smartphones
- TV Equipment Related to Digital Television Services
- Telephony Services and Related Equipment
- Access to Audio-Visual Media Services
- Services Related to Air, Bus, Rail, and Waterborne Passenger Transport
- Banking Services
- E-Books
- E-Commerce
These sectors were identified as essential for individuals with disabilities and are most likely to have divergent accessibility requirements across EU countries.
EU Member State Compliance
EU member states are required to transpose the EAA into their national laws by June 28, 2022, and to apply these requirements to products and services by June 28, 2025. This timeline ensures that businesses have sufficient time to comply with the new standards
Member States' Responsibilities
Each member state is responsible for:
- Implementing National Legislation: Adopting laws and regulations that align with the EAA's requirements.
- Monitoring Compliance: Establishing procedures to check the compliance of services with the EAA, following up on complaints or reports of non-compliance, and verifying that any identified issues have been duly remedied.
- Enforcement: Ensuring that penalties for non-compliance are effective, proportionate, and dissuasive.
Outside the EU
While the EAA applies to EU member states, its influence extends beyond the EU. Organizations outside the EU that provide products or services to consumers within the EU are also required to comply with the EAA's accessibility standards. This extraterritorial application ensures that individuals with disabilities have equal access to products and services, regardless of the provider's location
Understanding the Impact of the European Accessibility Act
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) is a pivotal directive aimed at harmonizing accessibility standards across the European Union (EU), ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal access to products and services. By establishing common rules, the EAA seeks to eliminate barriers created by divergent national regulations, thereby enhancing the functioning of the internal market for accessible products and services
Barrier-Free Access
The EAA mandates that a range of products and services, including consumer electronics, ticketing and vending machines, websites, and mobile applications, comply with accessibility requirements. This ensures that individuals with disabilities can access and use these services without encountering barriers.
Accessibility Features
To meet the EAA's standards, businesses are required to implement specific accessibility features in their products and services. These features are designed to accommodate the diverse needs of individuals with disabilities, promoting inclusivity and equal participation in society.
Accessible Products and Services
The EAA covers products and services that have been identified as most important for persons with disabilities and are most likely to have diverging accessibility requirements across EU countries. By harmonizing these requirements, the EAA aims to improve the availability and quality of accessible products and services in the market
Services in the Market
The implementation of the EAA is expected to lead to more accessible products and services in the market, benefiting both businesses and consumers. Businesses will benefit from common rules on accessibility in the EU, leading to cost reduction, easier cross-border trading, and more market opportunities for their accessible products and services. Persons with disabilities and elderly people will benefit from more accessible products and services at more competitive prices, fewer barriers when accessing transport, education, and the open labor market, and more jobs available where accessibility expertise is needed.
Services in the EU
The EAA aims to improve the functioning of the internal market for accessible products and services by removing barriers created by divergent legislation. This will lead to a more inclusive market where individuals with disabilities can access a wider range of services across the EU


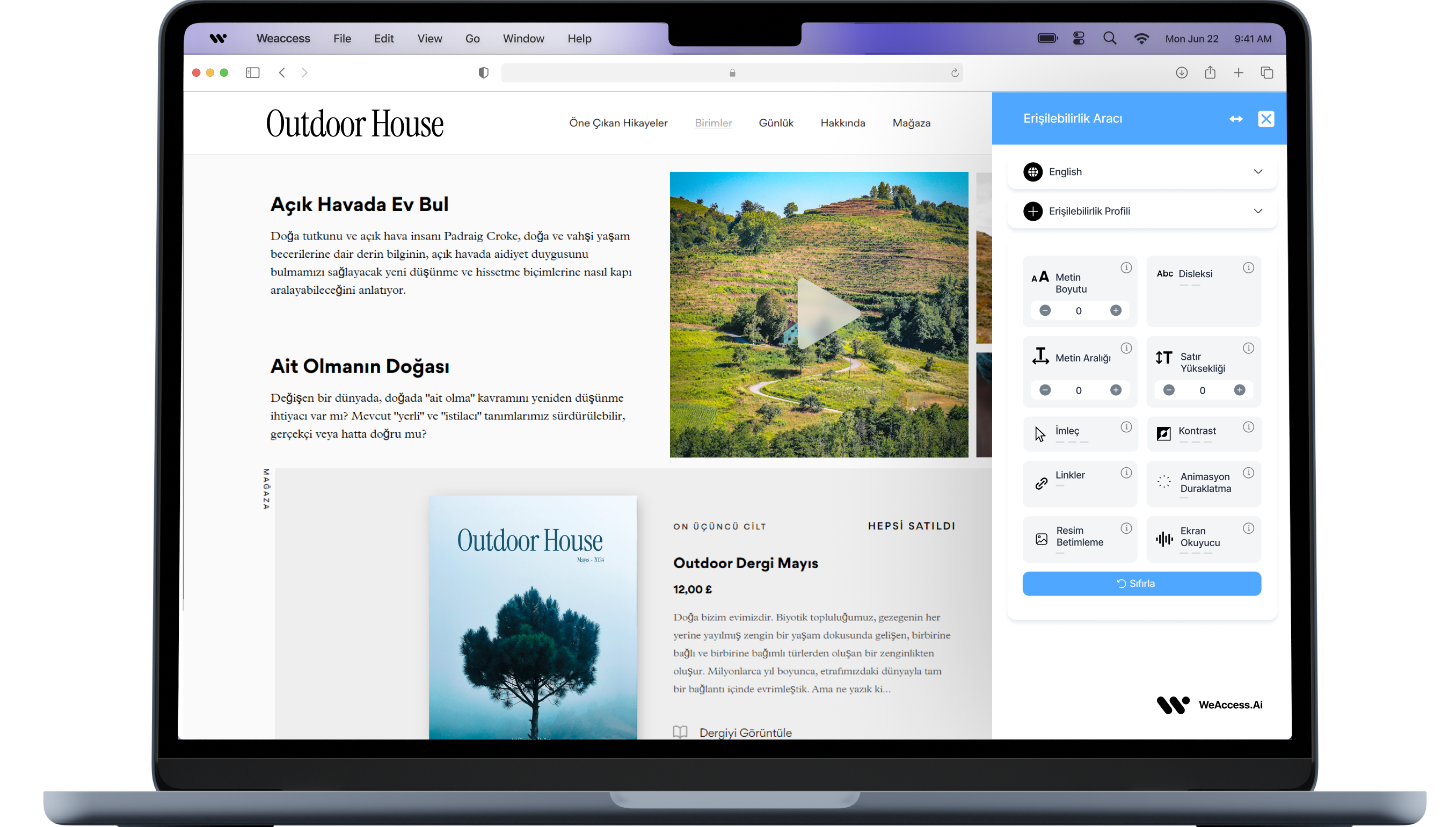
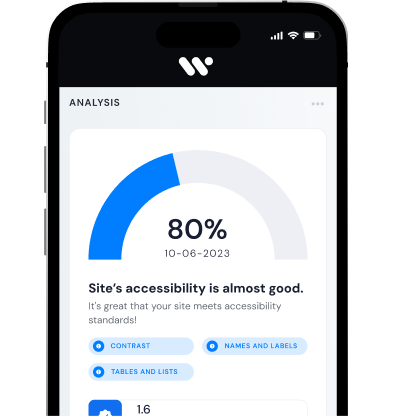
 Web Accessibility Suite
Inclusive, accessible web for all.
Web Accessibility Suite
Inclusive, accessible web for all.


 Mobile Accessibility Suite
Smooth access on mobile devices.
Mobile Accessibility Suite
Smooth access on mobile devices.


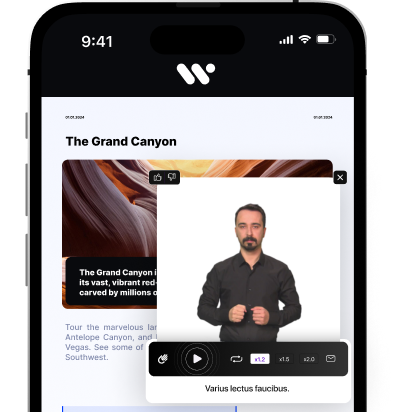
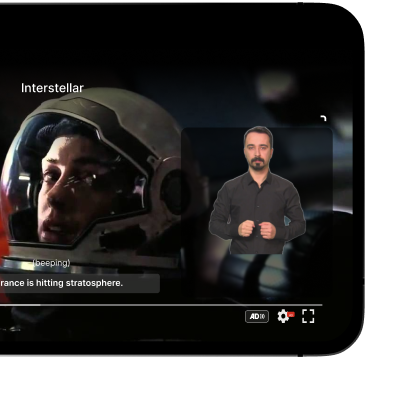
 Media Accessibility Suite
Accessible videos and images for all.
Media Accessibility Suite
Accessible videos and images for all.


 Document Accessibility Suite
Accessible PDFs for all.
Document Accessibility Suite
Accessible PDFs for all.


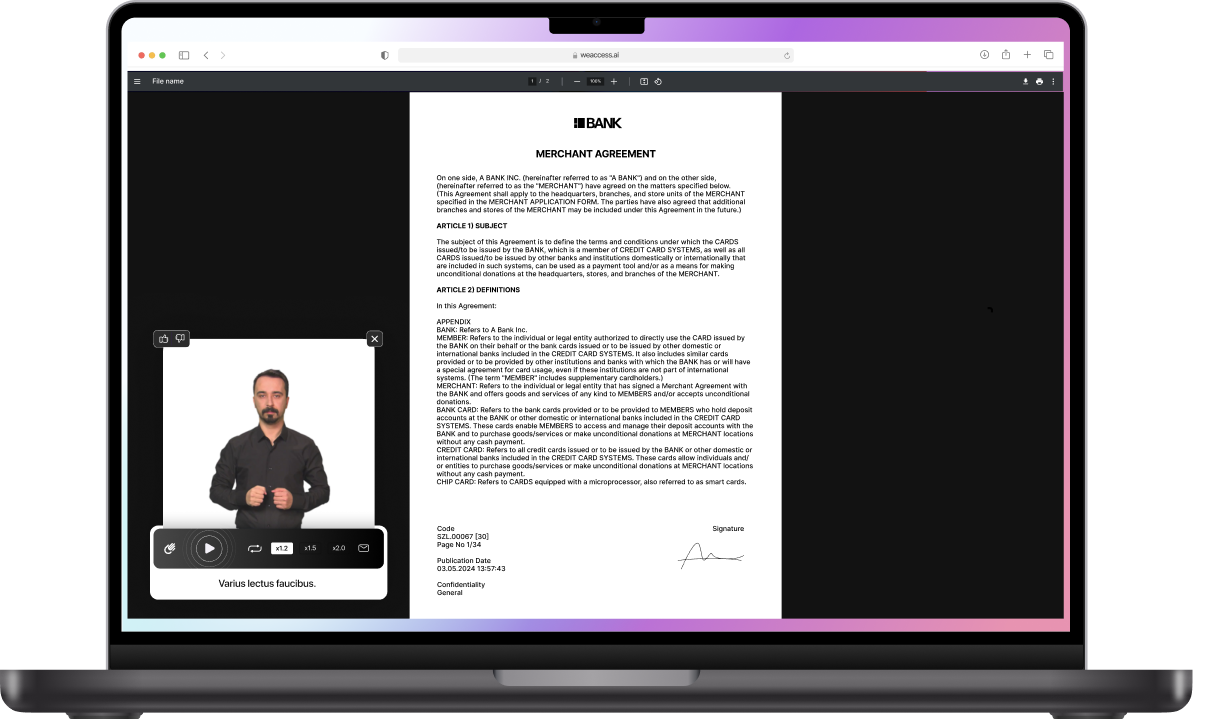
 Printed Content Accessibility Suite
Accessible print, audio description, voiceover, & sign language support.
Printed Content Accessibility Suite
Accessible print, audio description, voiceover, & sign language support.